Localizing Web Applications
PUBLISHED
Localization is the process of adapting your application for a specific region or language. Localization allows the application access to different resources without source code changes.
Because a single language can be used in multiple parts of the world, your application must adapt to the regional and cultural conventions of where the application users reside.
Tizen Studio provides several technologies to help you develop an internationalized application. The Web Localization view is a tool which helps you localize strings, resources, and content of a Tizen Web project.
This topic describes how to localize your application.
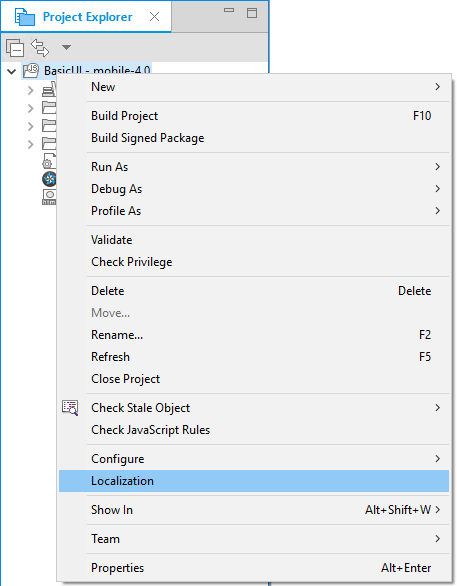
Opening the Web Localization View
To open the Web Localization view:
- Right-click the selected project in the Project Explorer view.
- Click Localization.
Figure: Opening the Web Localization view
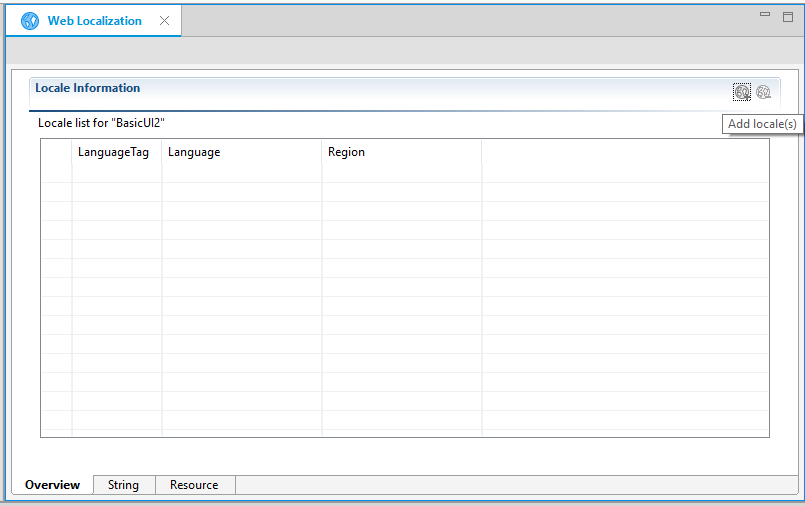
Adding Locales
To use localized strings and resource content, you must add locales for them:
- Click the Add locale(s) button (
 ).
).
- In the New Target Locale table, select the locales you want.
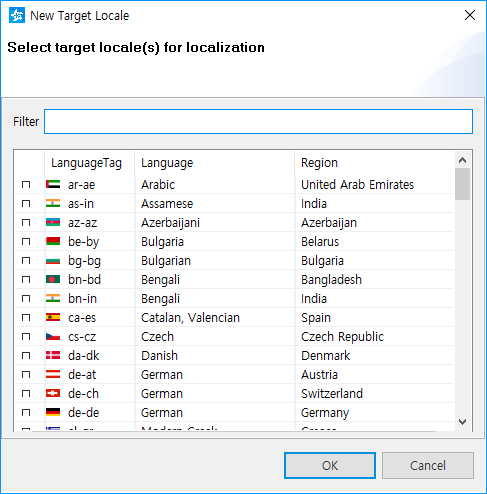
- To confirm the selected locale information, click OK.
Figure: Added locales
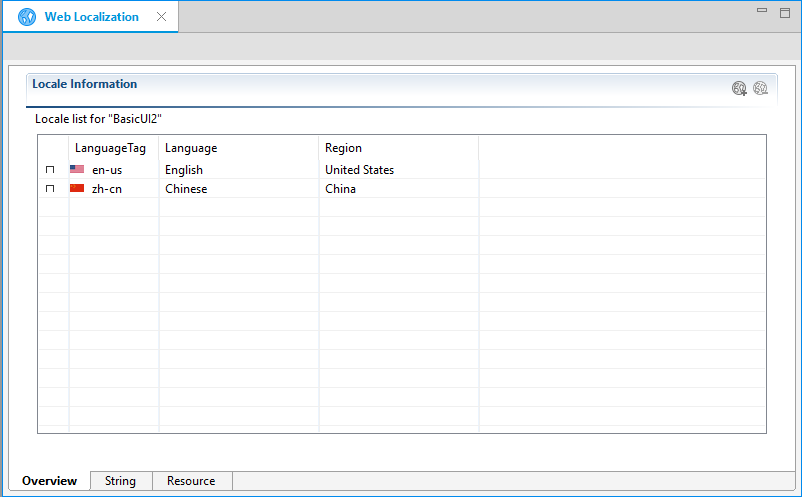
A container named locales is created for the localized content. Under the container, a subfolder for a locale is added when you set a locale. For example, /locales/en-us and /locales/zn-cn.
Creating and Managing Localized Strings
To localize and handle strings, use the String tab:
- To add a localized string, click the Add localization button (
 ) on the toolbar.
) on the toolbar.
- In the New Localization dialog, enter the identifier for the localized string content. In the table, enter values for the default locale and all the locales you have specified in the Overview tab.
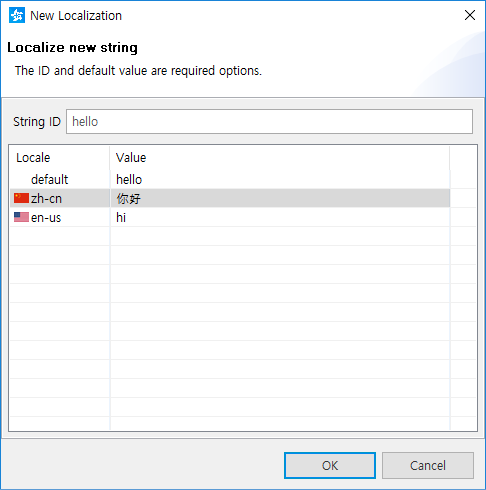
- To save the localized string content, click OK.
You can check the defined strings in the String tab.
Figure: Defined strings
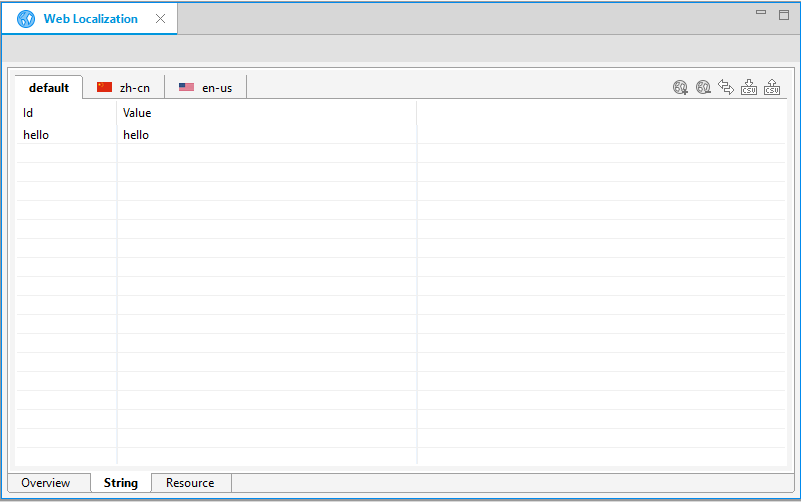
You can add more items to the table or remove them, as needed.
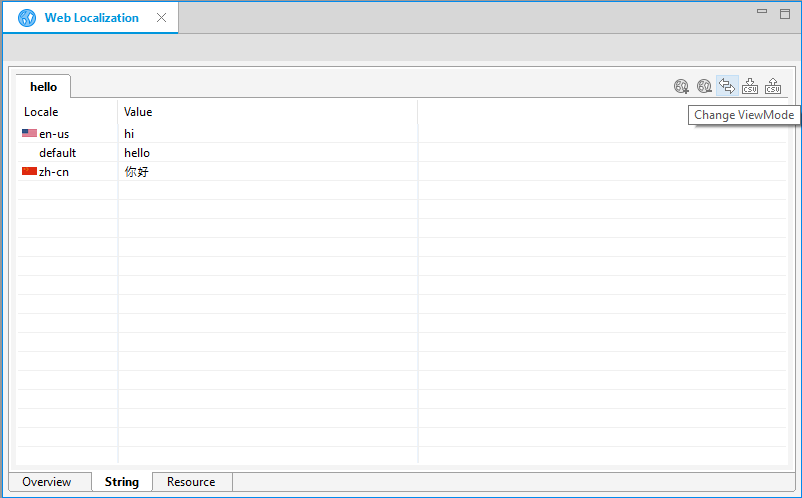
You can change the table tab configuration between ID and Locale by clicking the Change ViewMode button (![]() ).
).
Figure: String-based viewmode
When the string localization is complete, the following modifications are made in the project:
language.jsfile is created in the application's top-level folder and in each locale folder underlocales, containing the localized string content.Figure: language.js
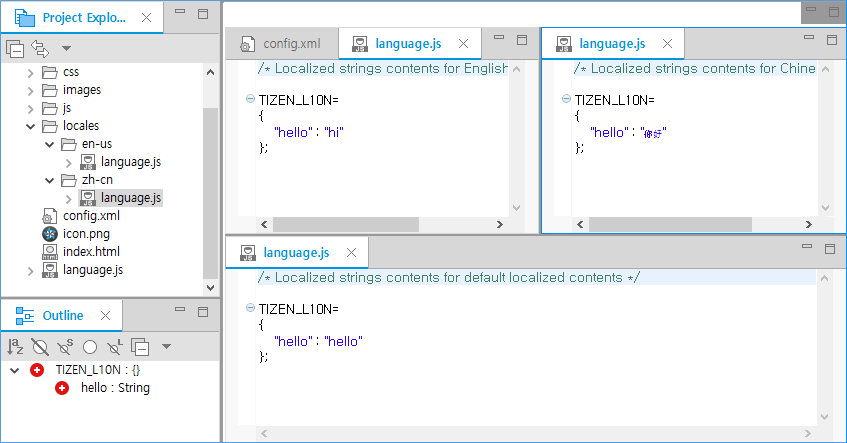
- The
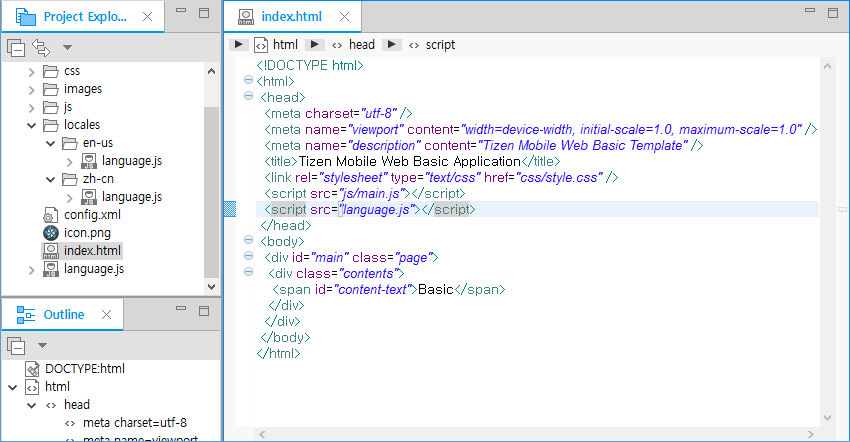
<script>element, whosesrcattribute islanguage.js, is added to theindex.htmlfile.
Figure: src element in index.html
For more information on using localized string content, see Localization.
Using Resources for Localization
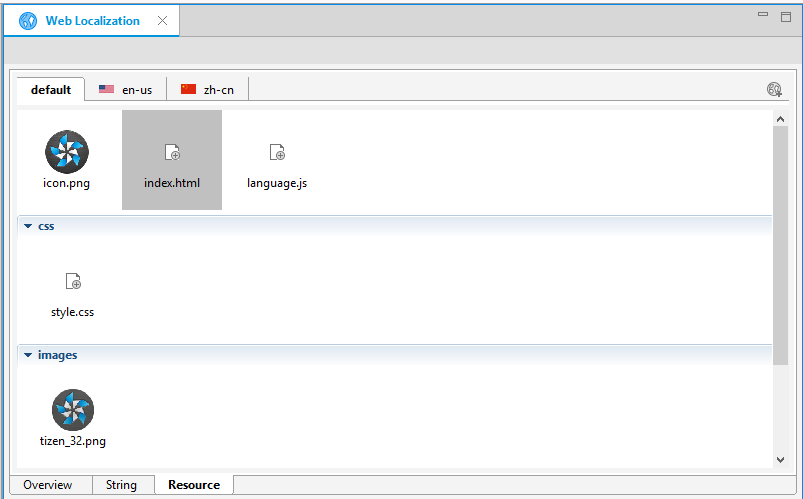
In the Resource tab, you can localize resource files, such as images, sound, video, HTML, and JavaScript more efficiently. The Resource tab displays the resources of the project in a tile form.
Figure: Resource tab
If a resource is not localized, the + button appears on the resource tile.
Figure: Missing resource file

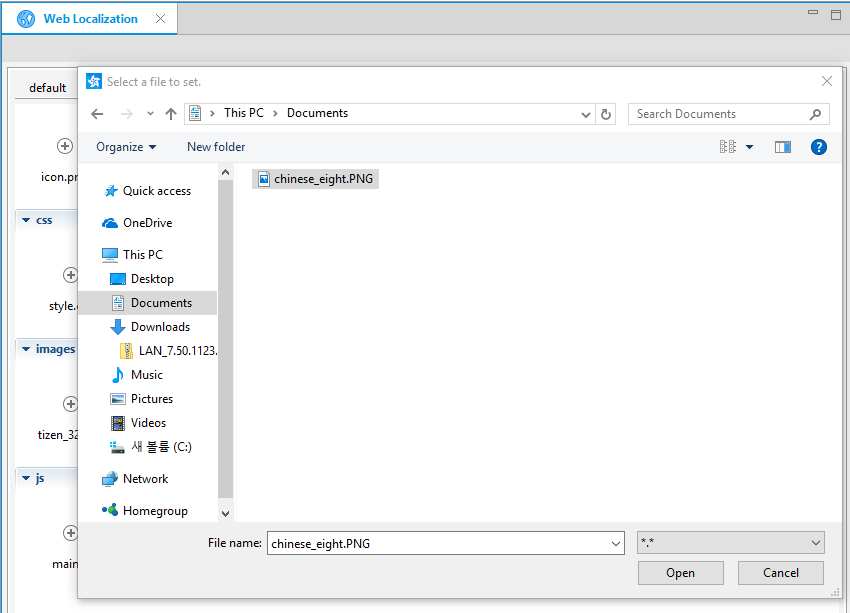
To localize the missing resource:
- Click the + button on the resource tile.
- In the Select a file to set dialog, select a new resource to replace the default resource, and click OK.
The complex folder structures are created and the names of the resource files are replaced.
Folder-based Localization
Folder-based localization places the resources inside locale folders with names determined by the language tag, such as en-us and ko-kr. The locale folders are located under a container folder named locales. The localized resources are used depending on the location settings of the device. If there are no localized resources, the default resource is used.
For example, if the locale of a device is ko-kr, the images/a.png and images/c.png images are replaced with the locales/ko-kr/images/a.png and locales/ko-kr/images/c.png images. However, the images/b.png image is not replaced, because there is no applicable resource in the locales/ko-kr/images/ folder.
root/
images/
a.png
b.png
c.png
locales/
ko-kr/
images/
a.png
c.png
