Near Field Communication (NFC)
PUBLISHED
The Near Field Communication (NFC) service enables information exchange between NFC-enabled devices (called "peers") or tags. The NFC-enabled devices can share contacts, photos, and videos, and can also act as smart cards. You can use an NFC-enabled device to send NDEF messages to NFC tags to implement a variety of activities, such as paying the grocery bill or downloading a coupon. With application controls, you can launch NFC applications when NFC-related operations occur.
This feature is supported in mobile and wearable applications only.
The main features of the NFC API include:
- NFC device management
You can manage NFC connectivity by enabling or disabling the NFC service.
- NFC tag and peer detection
You can receive notifications when an NFC tag or peer device has been detected.
- NDEF message manipulation
You can handle NDEF messages by first creating NDEF records, and then adding the records to an NDEF message.
- NDEF data exchange
- NFC card emulation
You can enable NFC card emulation and monitor the secure element transaction carried out by the device.
- NFC host-based card emulation (HCE)
You can handle HCE events and transactions.
NFC provides the following advantages over short-range communication technologies, such as Bluetooth:
- Faster set-up
- Lower power consumption
- No device pairing requirements
- Reduction in unwanted interruptions
NFC Tags and NDEF Messages
An NFC tag is a chip which can securely store personal information, such as debit card numbers or contact details. The methods of the NFCTag interface (in mobile and wearable applications) are used to access an NFC tag for reading or writing information. NFC tag types are identified using the type attribute of the NFCTagType type definition (in mobile and wearable applications).
GENERIC_TARGET, ISO14443_A, ISO14443_4A, ISO14443_3A, MIFARE_MINI, MIFARE_1K, MIFARE_4K, MIFARE_ULTRA, MIFARE_DESFIRE, ISO14443_B, ISO14443_4B, ISO14443_BPRIME, FELICA, JEWEL, ISO15693, and UNKNOWN_TARGET.The NFC forum defines the NFC data exchange format (NDEF) for encapsulating the data exchanged between 2 NFC-enabled devices or an NFC-enabled device and an NFC tag. An NDEF message can store data in various formats, such as text, Multipurpose Internet Mail Extension (MIME) type object, or ultra-short RagTime Document (RTD). The NFC tags use NDEF for exchanging messages. Tizen provides the NDEFMessage interface (in mobile and wearable applications) to define an NDEF message.
An NDEF message is composed of multiple records. An NDEF record is created using the NDEFRecord interface (in mobile and wearable applications) and is identified by record type, ID, and payload. The following figure shows the conceptual structure of an NDEF message.
Figure: Structure of an NDEF message
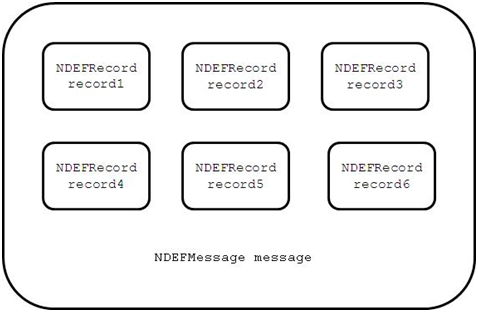
A record in an NDEF message can be created by using the following payload types:
- Text
The NDEF record content is created using text format.
The
NDEFRecordTextinterface (in mobile and wearable applications) is used to create the text format payload using thetext,languageCode, andencodingattributes. - URI
The NDEF record content is created using a URI.
The
NDEFRecordURIinterface (in mobile and wearable applications) is used to create the URI type payload using theuriattribute. - Media
The NDEF record content is created using a media format.
The
NDEFRecordMediainterface (in mobile and wearable applications) is used to create the media format payload using themimeTypeattribute.
Prerequisites
To use the Application (in mobile and wearable applications) and NFC (in mobile and wearable applications) APIs, the application has to request permission by adding the following privileges to the config.xml file:
<tizen:privilege name="http://tizen.org/privilege/application.launch"/> <tizen:privilege name="http://tizen.org/privilege/nfc.cardemulation"/> <tizen:privilege name="http://tizen.org/privilege/nfc.common"/> <tizen:privilege name="http://tizen.org/privilege/nfc.p2p"/> <tizen:privilege name="http://tizen.org/privilege/nfc.tag"/>
Managing NFC Connectivity
To use NFC, retrieve the default NFC adapter using the getDefaultAdapter() method of the NFCAdapter interface (in mobile and wearable applications).
To enable or disable the NFC service:
-
To get the default NFC adapter, use the
getDefaultAdapter()method and prepare anApplicationControlobject (in mobile and wearable applications) to request the NFC switching operation:var nfcSwitchAppControl = new tizen.ApplicationControl('http://tizen.org/appcontrol/operation/setting/nfc'); var adapter = tizen.nfc.getDefaultAdapter(); - Define the event listener for the
launchAppControl()method:
function launchSuccess() { console.log('NFC Settings application has successfully launched.'); } function launchError(error) { alert('An error occurred: ' + error.name + '. Please enable NFC through the Settings application.'); } - Define the event handler for an application control, which implements the
ApplicationControlDataArrayReplyCallbackinterface (in mobile and wearable applications):
var serviceReply = { /* onsuccess is called when the launched application reports success */ onsuccess: function(data) { if (adapter.powered) { console.log('NFC is successfully turned on.'); } }, /* onfailure is called when the launched application reports failure of the requested operation */ onfailure: function() { alert('NFC Settings application reported failure.'); } } - If necessary, request launching the NFC Settings with
nfcSwitchAppControlas a parameter:
if (adapter.powered) { console.log('NFC is already enabled'); } else { console.log('Try to launch the NFC Settings application.'); tizen.application.launchAppControl(nfcSwitchAppControl, null, launchSuccess, launchError, serviceReply); }
Detecting NFC Tags and Peer Devices
To receive notifications when an NFC tag or peer device has been detected, register event listeners with the setTagListener() and setPeerListener() methods of the NFCAdapter interface (in mobile and wearable applications). You can use the NFCTagDetectCallback (in mobile and wearable applications) and NFCPeerDetectCallback (in mobile and wearable applications) interfaces to define event handlers for receiving the notifications about attaching and detaching NFC tags and peers, respectively.
To detect NFC tags and peer devices:
-
To get the default NFC adapter, use the
getDefaultAdapter()method:var nfcAdapter = tizen.nfc.getDefaultAdapter();
-
Define the event handlers for NFC tag detection using the
NFCTagDetectCallbacklistener interface:var setTagDetect = { /* When an NFC tag is detected */ onattach: function(nfcTag) { console.log('NFC Tag detected. Its type is: ' + nfcTag.type); }, /* When an NFC tag becomes unavailable */ ondetach: function() { console.log('NFC Tag unavailable'); } } -
Register the listener to use the defined event handlers.
You can limit the listener to detect only specific NFC tag types by defining the tag types as the second parameter of the
setTagListener()method. In the following example, only MIFARE tags are detected./* Defines the tag types to be detected */ var tagFilter = ['MIFARE_MINI', 'MIFARE_1K', 'MIFARE_4K', 'MIFARE_ULTRA', 'MIFARE_DESFIRE']; /* Registers the event listener */ nfcAdapter.setTagListener(setTagDetect, tagFilter);
-
To stop the tag detection, use the
unsetTagListener()method:nfcAdapter.unsetTagListener();
NFC peers are detected similarly as NFC tags, except that the setPeerListener() method is used to register the NFCPeerDetectCallback listener interface, and the unsetPeerListener() method is used to stop the peer detection.
Handling NDEF Messages
You can handle NDEF messages by first creating NDEF records using the NDEFRecord interface (in mobile and wearable applications), and then adding the records to an NDEF message using the records attribute of the NDEFMessage interface (in mobile and wearable applications).
To create NDEF messages:
-
To create an NDEF URI record, create an
NDEFRecordURIinterface instance (in mobile and wearable applications) and specify the URI parameter.Additionally, you can create instances of the
NDEFRecord,NDEFRecordText(in mobile and wearable applications), orNDEFRecordMedia(in mobile and wearable applications) interfaces based on the record type to be created.var newRecord = new tizen.NDEFRecordURI('https://www.tizen.org/'); -
Create an
NDEFMessageinterface instance:var newMessage = new tizen.NDEFMessage();
-
To add an NDEF record to an NDEF message, use the
recordsattribute of theNDEFMessageinterface:newMessage.records[0] = newRecord;
Exchanging NDEF Data with Peers
To exchange data between peers, the setReceiveNDEFListener() method of the NFCPeer interface (in mobile and wearable applications) registers an event listener, which triggers an event when an NDEF message is received from a peer.
You can use the NDEFMessageReadCallback interface (in mobile and wearable applications) to define event handlers for reading NDEF messages from peer devices.
To exchange NDEF messages:
-
To receive NDEF messages from a peer device, use the
setReceiveNDEFListener()method of theNFCPeerinterface.The
setReceiveNDEFListener()method registers theNDEFMessageReadCallbacklistener interface, which is invoked when an NDEF message from a peer device is read./* NDEFMessageReadCallback listener */ function readMessage(message) { console.log('Record Count is ' + message.recordCount); } /* Set a listener to receive an NDEF message */ Peer.setReceiveNDEFListener(readMessage); -
To send an NDEF message to an NFC peer, use the
sendNDEF()method:var newMessage = new tizen.NDEFMessage(); Peer.sendNDEF(newMessage);
sendNDEF() method, an error callback is launched. This method can only be used on the foreground.Exchanging NDEF Data with Tags
To exchange data between tags, you can read from tags and write to tags using the readNDEF() and writeNDEF() methods.
You can use the NDEFMessageReadCallback interface (in mobile and wearable applications) to define event handlers for reading NDEF messages from tags.
To exchange NDEF data with tags:
-
To read data from an NFC tag, use the
readNDEF()method of theNFCTaginterface (in mobile and wearable applications).The
readNDEF()method registers theNDEFMessageReadCallbacklistener interface, which is invoked when an NDEF message is read./* NDEFMessageReadCallback listener */ function readMessage(message) { console.log('Record Count is ' + message.recordCount); } /* Check whether the NFC tag supports NDEF format */ if (Tag.isSupportedNDEF) { /* Read NDEF data */ Tag.readNDEF(readMessage); } -
To write data on an NFC tag, use the
writeNDEF()method:var newMessage = new tizen.NDEFMessage(); function writeCallback() { console.log('Success!'); } Tag.writeNDEF(newMessage, writeCallback);You can use the
transceive()method to transfer raw data as a byte array to an NFC tag without knowing the underlying details of the tag.
writeNDEF() or transceive() method, an error callback is launched. These methods can only be used on the foreground.Using NFC Card Emulation
You can enable NFC card emulation and monitor the secure element transaction taking place using the NFCAdapter interface (in mobile and wearable applications). The secure element transaction is carried out by the device. The Tizen application can detect the transaction, but does not take part in it. Interpreting the transaction data requires knowledge about the data protocol the transaction uses. With the required knowledge, the application can detect whether the transaction was successful.
To enable or disable the NFC card emulation and detect secure element transactions:
- Declare the required variables and obtain the
NFCAdapterobject using thegetDefaultAdapter()method of theNFCManagerinterface (in mobile and wearable applications):var adapter = tizen.nfc.getDefaultAdapter(); var modeListenerId = 0, aseListenerId = 0, transListenerId = 0;
- Use the
addCardEmulationModeChangeListener()method of theNFCAdapterinterface to register a listener to monitor the current card emulation mode:
modeListenerId = adapter.addCardEmulationModeChangeListener(function(mode) { if (mode === 'ALWAYS_ON') { console.log('We are ready to go now'); } }); - To enable NFC card emulation, change the value of the
cardEmulationModeattribute:
adapter.cardEmulationMode = 'ALWAYS_ON';
- To be notified when the type of an active NFC secure element changes, use the
addActiveSecureElementChangeListener()method of theNFCAdapterinterface:
aseListenerId = adapter.addActiveSecureElementChangeListener(function(seType) { console.log('Active secure element is ' + seType); }); - To be notified when a NFC secure element transaction data is exchanged, use the
addTransactionEventListener()method of theNFCAdapterinterface:
function onDetected(appletId, data) { console.log('NFC secure element transaction detected. Application: ' + appletId + '. Protocol data: ' + data); }; transListenerId = adapter.addTransactionEventListener('UICC', onDetected); - Remove the registered listeners when they are no longer necessary and disable NFC card emulation:
adapter.removeActiveSecureElementChangeListener(aseListenerId); adapter.removeTransactionEventListener(transListenerId); adapter.removeCardEmulationModeChangeListener(modeListenerId); adapter.cardEmulationMode = 'OFF';
Using NFC Host-based Card Emulation
You can handle HCE (host-based card emulation) events and transactions taking place using the NFCAdapter interface (in mobile and wearable applications). HCE is an on-device technology that permits a phone to perform card emulation on an NFC-enabled device without relying on access to a secure element. The transaction data is routed to the host application directly, instead of routing to a secure element. The Tizen application can detect the transaction and can take part in it.
To detect NFC HCE events and manage AID (Application ID):
-
Specify an
AIDvalue for receiving HCE transaction events:-
To tell the platform which AID groups are requested by the application, a metadata element must be included in the
config.xmlfile:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <widget xmlns:tizen="http://tizen.org/ns/widgets" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/ns/widgets" id="http://yourdomain/NFCtest" version="1.0.0" viewmodes="maximized"> <profile name="wearable"/> <tizen:application id="ZmAk4fxZWY.NFCtest" package="ZmAk4fxZWY" required_version="2.3.1"/> <icon src="icon.png"/> <name>NFCtest</name> <tizen:privilege name="http://tizen.org/privilege/nfc.common"/> <tizen:privilege name="http://tizen.org/privilege/nfc.cardemulation"/> <tizen:app-control> <tizen:src name="index.xml" reload="enable"/> <tizen:operation name="http://tizen.org/appcontrol/operation/nfc/card_emulation/host_apdu_service"/> <tizen:uri name="nfc://secure/HCE/aid/A0000000041010"/> </tizen:app-control> <tizen:metadata key="http://tizen.org/metadata/nfc_cardemulation" value="/res/wgt/wallet.xml"/> </widget>- The
tizen:app-controlelement must contain thetizen:srcandtizen:operationandtizen:urielements:- The
tizen:srcelement must contain thenameattribute that defines the page to be handled. Thereloadattribute is optional. - The
tizen:operationelement must behttp://tizen.org/appcontrol/operation/nfc/card_emulation/host_apdu_service. - The
tizen:urielement must benfc://secure/HCE/aid/<specific AID>.
- The
- The
tizen:metadataelement must contain thekeyandvalueattributes:- The
keyattribute must behttp://tizen.org/metadata/nfc_cardemulation. - The
valueattribute must contain the AID XML file path.The
valueattribute is a relative path starting from the application root path.
- The
- The
-
The metadata element points to an AID XML file. The following is an example of the file with an AID declaration:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <application name="NFCtest"> <wallet> <aid-group category="payment"> <aid aid="A0000000041010" se_type="hce" unlock="false" power="on"/> </aid-group> <aid-group category="other"> <aid aid="D4100000030001" se_type="hce" unlock="false" power="on"/> </aid-group> </wallet> </application>- The
applicationelement must contain anameattribute with an application name. - The
applicationelement must contain 1 or morewalletelements, each of which must contain 1 or moreaid-groupelements. - The
aid-groupelement is required to contain acategoryattribute with thepaymentorothervalue. - Each
aid-groupelement must contain 1 or moreaidelements, each of which contains a single AID. Theaid-groupcan have as manyaidelements as you want. - The
aidelement must contain theaid,se_type,unlock, andpowerattributes. - The
se_typeattribute must containhce,ese, oruicc. These_typevalue can be added later. - The
unlockattribute must contain one of the following:true: The card cannot work when the device is locked.false: The card can work when the device is locked.
- The
powermust contain one of the following:on: The card can work when the device is on.off: The card can work when the device is off.sleep: The card can work when the device is in the sleep mode.
- The
-
-
Declare the required variables and obtain the
NFCAdapterobject using thegetDefaultAdapter()method of theNFCManagerinterface (in mobile and wearable applications).To enable NFC card emulation, change the value of the
cardEmulationModeattribute.var hceListenerId = 0; var adapter = tizen.nfc.getDefaultAdapter(); adapter.cardEmulationMode = 'ALWAYS_ON';
-
To detect the HCE event, use the
addHCEEventListener()method of theNFCAdapterinterface to register a listener.Use the
sendHostAPDUResponse()method of theNFCAdapterinterface to send a host APDU response to a contactless front-end. (APDU - Application Protocol Data Unit - is defined in the ISO/IEC 7816-4 specification.)var successCB = function() { console.log('Sending APDU response was successful.'); }; var errorCB = function() { console.log('Sending APDU response failed.'); }; hceListenerId = adapter.addHCEEventListener(function(event_data) { if (event_data.eventType == 'ACTIVATED') { console.log('HCE activated'); } else if (event_data.eventType == 'DEACTIVATED') { console.log('HCE deactivated'); } else if (event_data.eventType == 'APDU_RECEIVED') { console.log('APDU received'); var apdu_response = [0x00, 0xA4, 0x04, 0x00, 0x04, 0x11, 0x12, 0x13, 0x14]; adapter.sendHostAPDUResponse(apdu_response, successCB, errorCB); } }); - To register an AID for a specific category and secure element type, use the
registerAID()method of theNFCAdapterinterface:
try { var aid = 'ABC0012345'; adapter.registerAID('HCE', aid, 'PAYMENT'); } catch (err) { console.log(err.name + ':' + err.message); } - To retrieve the registered AIDs for a specific category and secure element type, use the
getAIDsForCategory()method of theNFCAdapterinterface:
try { var successCallback = function(aid_datas) { for (var i = 0; i < aid_datas.length; i++) { console.log('SE Type is ' + aid_datas[i].type); console.log('AID is ' + aid_datas[i].aid); console.log('readonly: ' + aid_datas[i].readOnly); } }; var errorCallback = function(error) { console.log('getAIDsForCategory failed.'); }; adapter.getAIDsForCategory('HCE', 'PAYMENT', successCallback, errorCallback); } catch (err) { console.log(err.name + ':' + err.message); } - Remove the registered listeners when they are no longer necessary, and disable NFC card emulation:
adapter.removeHCEEventListener(hceListenerId); adapter.cardEmulationMode = 'OFF';
Since Tizen 4.0, you can change the routing priority of NFC card emulation events. The card emulation events can be sent to the application currently on the foreground (instead of the application chosen in NFC settings), as long as the application stays on the foreground.
To set your application as preferred for HCE events, call the setPreferredApp() method of the NFCAdapter interface. When the application leaves the foreground, it loses the preferred application status, and when it enters the foreground again, it regains the status. For more information on this behavior, see the setPreferredApp() method in the NFCAdapter interface.
When an application no longer needs to receive card emulation events, change the routing priority back to the default setting by calling the unsetPreferredApp() method.
NFC Application Control Operations
You can launch NFC applications based on the NDEF message content using the application control functionalities:
- NFC application can be launched by the receipt of an NDEF message or by the reading of an NFC tag.
If the application control with the
http://tizen.org/appcontrol/operation/nfc/wellknownoperation is defined in theconfig.xmlfile and an NFC-enabled device reads an NFC tag or receives an NDEF message whose first NDEF record has a record type (tnfvalue) set asNFC_RECORD_TNF_WELL_KNOWN, the NFC application is launched. - NFC applications can be launched by the transaction of the card emulation functionality. NFC devices can communicate with point of sales (POS) terminals using the card emulation functionality to, for example, make a payment.
If the application control with the
http://tizen.org/appcontrol/operation/nfc/transactionorhttp://tizen.org/appcontrol/operation/nfc/off_host_apdu_serviceoperation is defined in theconfig.xmlfile and a secure element transaction occurs, the NFC application is launched. - NFC applications can be launched by the transaction of the HCE functionality. The NFC application can communicate with point of sales (POS) terminals using the HCE functionality to, for example, make a payment.
If the application control with the
http://tizen.org/appcontrol/operation/nfc/host_apdu_serviceoperation is defined in theconfig.xmlfile and an HCE transaction occurs, the NFC application is launched. - The system sends the
http://tizen.org/appcontrol/operation/nfc/card_emulation/default_changedapplication control event when the default wallet is changed. For example, in Setting > NFC > Set Default Wallet App, if the default wallet is changed, an application control with this operation is sent to the selected application (wallet).
The following table lists the NFC operations, URI scheme and MIME.
Table: NFC operations
| Operation | URI scheme | MIME |
|---|---|---|
http://tizen.org/appcontrol/operation/nfc/empty |
NULL |
NULL |
http://tizen.org/appcontrol/operation/nfc/wellknown |
<scheme>:<host>/<path>
URL, for example:
URN, for example:
|
U/<protocol_code>
For example: |
NULL |
<type_string>/*
For example: |
|
http://tizen.org/appcontrol/operation/nfc/mime |
NULL |
<type_string>/<subtype_string> (case-insensitive)
For example: |
http://tizen.org/appcontrol/operation/nfc/uri |
<uri>
For example: |
NULL |
http://tizen.org/appcontrol/operation/nfc/external |
<scheme>:<string> (case-insensitive)
For example: |
NULL |
http://tizen.org/appcontrol/operation/nfc/transaction |
nfc://secure/<SE name>/aid/<aid>
For example:
|
NULL |
http://tizen.org/appcontrol/operation/nfc/card_emulation/host_apdu_service |
NULL |
NULL |
http://tizen.org/appcontrol/operation/nfc/card_emulation/off_host_apdu_service |
NULL |
NULL |
http://tizen.org/appcontrol/operation/nfc/card_emulation/default_changed |
NULL |
NULL |
* The <protocol_code> and <scheme> must be in sync. See NFCForum-TS-RTD_URI_1.0 and NFC RTD (Record Type Definition) documentation on the NFC forum.
