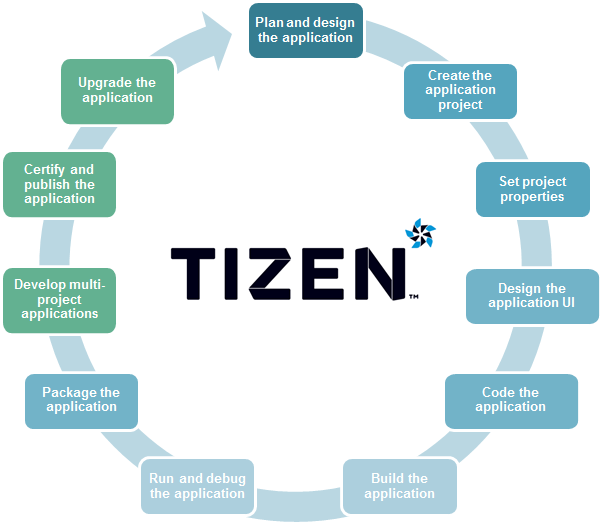
Web Application Development Process
Tizen provides the tools required to manage your application's life-cycle from product conception, through development and release, to end-of-life application retirement.
To develop an application with Tizen:
Planning and Designing the Application
The first step in creating a Tizen Web application is planning and designing it using the design tools of your choice.
For information on planning and designing your applications, see Tizen Web Guides and Tizen Web API References.
Once you have finished the application plan and design, you are ready to create the application project.
Creating the Application Project
After you have planned and designed your application, you are ready to create the application project in the Tizen IDE.
When creating the application project, use an applicable project template or sample. Based on the selection, the Tizen Web Project Wizard automatically creates basic functionalities that the application has to implement to be able to run. You can select from a variety of templates and samples. You can also create custom user templates.
Setting Project Properties
After creating the application project, you can configure the properties of the project and the Web application to achieve the required functionality and features for your application.
Designing the Application UI
You can design the application UI using the UI components defined in the Web UI Framework Reference.
Coding the Application
Code your application in the IDE using the APIs defined in the Web API References.
Once you have finished coding your application, you are ready to build your application.
Building the Application
When the IDE builds an application, the following process is executed:
- Validation check for:
- JavaScript
- CSS
- Compile for:
- Coffeescript
- Less
| Note |
|---|
About the output files:
|
If the project has errors, they are shown in the Problems and Project Explorer views after the build.
You can build a Web application automatically or manually:
- Automatic build:
In the IDE menu, select Project > Build Automatically.
If you select this option, whenever the source or a resource is changed and saved, the IDE automatically recognizes any saved changes and rebuilds the project source.
- Manual build:
In the IDE menu, select Project > Build Project.
You can build your project at your convenience. If you want to use the manual build, ensure that the Project > Build Automatically option is not selected.
| Note |
|---|
In the manual build mode:
|
To customize the application, set the build properties:
- JS validation
Set the options in the IDE menu: Window > Preferences > Tizen SDK > Web > Editor > JavaScript Editor.
- CSS validation
Set the options in IDE menu: Window > Preferences > Tizen SDK > Web > Editor > Css Editor.
Running and Debugging the Application
When the IDE runs or debugs the application, the following process is executed:
- Build automatically if no build has been created yet.
- Package.
The optimization process is only executed when you execute the packaging process.
- Execute the application to the Emulator or target device.
You can run your application in one of the following environments:
-
Emulator
The device Emulator, provided with the Tizen SDK, imitates the target environment running Tizen Web applications. Using this replicated environment, you can test your application before deploying it to the real target device.
-
Target Device
Running your application on a target device allows you to debug and test your application in a real-time environment.
-
Simulator
The Tizen Web simulator allows you to run application that use the Tizen Web APIs.
You can run the application smartly:
- You can use the Rapid Development Support (RDS) mode to run or test faster.
- You can use the live editing mode to test faster (debug mode does not support it).
For more information about the debugging process and tools, see Debugging Web Applications.
Packaging the Application
When the IDE packages the application, the following process is executed:
- Build automatically if no build has been created yet
- Optimize resources:
- Obfuscation (for JavaScript)
- Minification (for HTML, JavaScript, CSS, and PNG)
- Create the frame structure (for hybrid core applications).
- Make up resources (for hybrid core, font, and UI framework applications).
- Handle signing.
Web application packaging process is based on the W3C packaging and configuration.
You can package a Web application using the web-packaging command in the Command Line Interface (CLI), which is an IDE functional tool in the Tizen SDK:
web-packaging project.wgt project/
The Tizen Web SDK provides the functionality to package a Web application quickly in the required format and to set the package properties.
In the IDE menu, you can set the package properties in Project > Properties > Tizen SDK > Package by selecting the resources to be included in the package. For a Web application, you can set the properties in Project > Properties > Tizen SDK > Package > Web:
-
Set excluding optimization resources
You can minify your JavaScript, CSS, HTML, and PNG resources and put in an exclude file pattern that you do not want to optimize.
- Set hybrid application's main service application
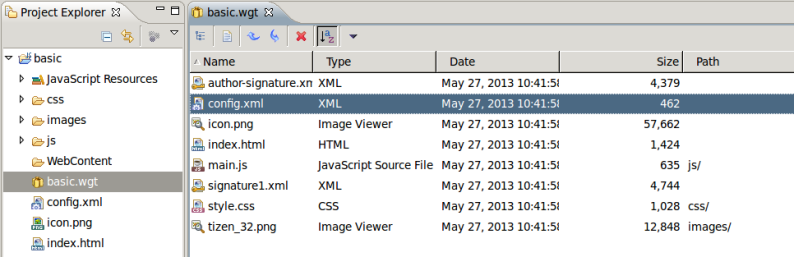
By default, the Web application package is created once. You can view the package content at any point of the application development process by double-clicking the project .wgt file in the Project Explorer view. All the files present in the application project are displayed in a list.
Any changes made to the files in the package content list, such as deleting files or dragging and dropping files, are not reflected in the actual project files.
Figure: Viewing the Web application package
Additionally, you can localize the Web application to support different languages and environments.
Developing Multiple Projects as a Combined Package
Tizen supports multi-project applications that combine different types of application templates in hybrid and companion applications.
Packaging Hybrid Applications
A hybrid application package combines a Web application and 1 or more native service applications.
To create and run a hybrid application:
- Create a project for a Web UI application and native service application.
- To establish a project reference between a UI and service application:
- In the Web UI application project context menu, select Properties > Project References.
- Select the check box for the service application, and click OK.
-
Build and run the Web UI application. The service application is built and executed automatically at the same time, and you can find a WGT file (hybrid application package) under the Web UI application project in the Project Explorer view.
To modify the build configuration of the service application, see Building the Application.
| Note |
|---|
| Tizen has limited a multi-project application combination policy for device usability. If you do not follow the policy, the submission of your application to the Tizen Store can be rejected. |
The following table shows the possible combinations for a hybrid multi-project. M means that multiple applications can be packaged as sub applications.
| Main project | Sub project | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UI | SERVICE | WATCH | WIDGET | |
| WEB UI | No | M | No | No |
| WEB SERVICE | No | No | No | No |
With a hybrid application package, you can register the included applications in the Tizen Store and install, upgrade, and uninstall them using the single hybrid package. When a hybrid application package is installed, the Web application is installed by the Web installer, followed by the native installer installing native service applications.
A hybrid application package is very useful to Web applications that need background processing or monitoring. A native service application does not have a UI and can be run in the background.
The Web application and native service applications within a hybrid application package share the same package ID and data folder. Sharing application data between them is easy. Many useful inter-application APIs, such as Message Port and AppControl, can be used in a hybrid application package.
For more information on hybrid applications and their package structure, see HybridWebApp and HybridServiceApp, and Hybrid Application Package.
Packaging Web Applications
A Web application package combines a Web application and 1 or more Web service applications.
| Note |
|---|
| Tizen has limited a multi-project application combination policy for device usability. If you do not follow the policy, the submission of your application to the Tizen Store can be rejected. |
The following table shows the possible combinations for a Web multi-project. M means that multiple applications can be packaged as sub applications. The STANDALONE column defines whether the application can be packaged alone as the main application.
| Main Project | Sub Project | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| STANDALONE | WEB UI | WEB SERVICE | |
| WEB UI | Yes | No | M |
| WEB SERVICE | No | No | No |
Certifying and Publishing the Application
After you have packaged your application, you are ready to certify and publish your application.
To certify and publish your application:
- Upload your mobile Web application to the Tizen Store or your wearable Web application to the Samsung Galaxy Apps Store for certification.
After the application is uploaded, the application is signed as a certified application installer package and the <Application_name>.wgt archive format, which contains the distributor signature, is added by the Tizen Store or Samsung Galaxy Apps Store.
- Check your application to the Tizen Store or Samsung Galaxy Apps Store for selling.
The Tizen Store or Samsung Galaxy Apps Store checks whether your application functions properly.
You can also upgrade your application after certification. If you want to withdraw your application from distribution and operation, you need to request for application retirement from the Tizen Store or Samsung Galaxy Apps Store.
Upgrading the Application
You can upgrade your application even after you have certified and made it available for sale at the Tizen Store or Samsung Galaxy Apps Store.
To upgrade your application:
- Update your application version, and if needed the privileges, in the config.xml configuration file in the IDE.
- Update the application code as needed.
- If needed, update the privileges in the config.xml configuration file in the IDE.
- Build, test, and repackage the application.
- Register the upgraded application on the Tizen Store or Samsung Galaxy Apps Store.
When a previously installed application is upgraded on a device, you can decide which data files from the old version are retained and which are deleted. The common Tizen upgrade policy is to overwrite all the application package files, while keeping the user-created files and directories unchanged.
Once your application has reached the end of its life-cycle, you can remove it from the Tizen Store or Samsung Galaxy Apps Store.
The following figure illustrates the process of developing a Tizen Web application.
Figure: Web application development process