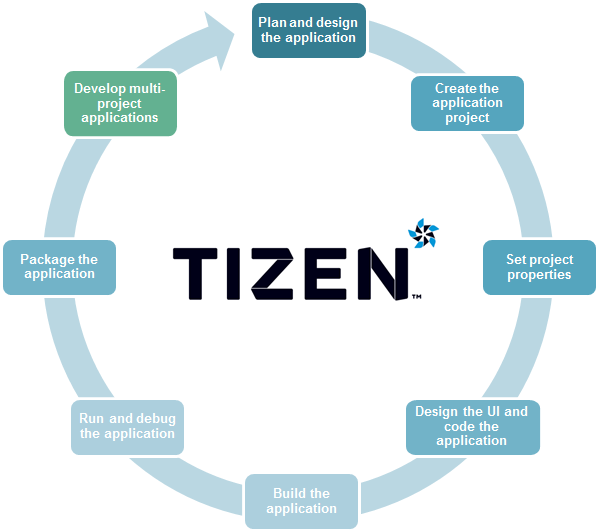
Native Application Development Process
Tizen provides the tools required to manage your application's life-cycle from product conception, through development and release, to end-of-life application retirement.
To develop an application with Tizen:
Planning and Designing the Application
The first step in creating a Tizen native application is planning and designing the application using the design tools of your choice.
Once you have finished the application plan and design, you are ready to create the application project.
Creating the Application Project
The Tizen IDE provides various project templates that make it easier for you to start coding your application. When you create a new project, you can select a specific template, which the Tizen native Project Wizard uses to automatically create basic functionalities that the native application implements to be able to execute. The default project files and folders are also created.
The following project templates are available:
-
UI Application
This template is suitable for creating a UI application with project files.
-
Service Application
This template is suitable for creating a service application that does not have an UI and always runs in the background. Service applications can also work with UI Application.
Setting Project Properties
After creating the application project, you can configure the project properties and create the application manifest to achieve the required functionality and features for your application.
Designing the Application UI and Implementing Code
Implementing your application consists of:
-
Designing and creating the application UI (User Interface)
You can design and create the application UI (user interface) with UI Builder.
UI Builder is included in the Tizen SDK, and functions as a WYSIWYG (What You See Is What You Get) design environment for creating UIs for native applications.
Note You can also design the application UI using the controls defined in UI guide. -
Coding applications
Code your application in the IDE using the namespaces defined in the Native API Reference.
If needed, update the privileges of the application.
Once you have finished implementing your application, you are ready to build your application.
Building the Application
You must build your native application project before you can run and debug the application.
The build configuration is the set of properties which are used in the build process. The build configuration includes the following properties:
- Build (compile and link) options
- Source files to build
- Compiler toolchain, such as compiler, linker, and archiver
Running and Debugging the Application
You can run your application in the Emulator. The device Emulator, provided with the Tizen SDK, imitates the target environment running Tizen native applications. Using this replicated environment, you can test your application before deploying it to the real target device.
You can also debug your application with the Emulator. The Emulator represents the almost identical functionality of the corresponding device model.
The Emulator provides the following debugging capabilities:
- Injecting events with the Event Injector view
- Simulating peripheral devices
- Acting as a source-level debugger
- Producing console output
You can make running and testing your application faster using the Rapid Development Support (RDS). For more information about the debugging methods and tools you can use, see Debugging Applications.
You can also optimize your application to achieve the best possible performance.
To debug your application with the Emulator or the target device, you must first build the application.
Packaging the Application
You can package your application using the Tizen IDE. If you want to register your application in the Tizen store, register the author certificate before packaging your application.
-
If you have made changes to the application after testing it, rebuild the application.
Select the project in the Project Explorer view.
In the project context menu, select Project > Build Package > TPK.
After the packaging is complete, check the package in the project folder to ensure that the packaging was successful.
Developing Multiple Projects as a Combined Package
Tizen supports multi-project applications that combine different types of application templates.
You can develop a UI project and service or shared library projects as a package.
To develop a multi-project native application:
- Create a UI application.
- Create a service application.
- Package a multi-project application using Tizen IDE:
- In the IDE, make sure all the applications you want to include in the package are located in the Project Explorer view.
To make the projects appear in the Project Explorer view, you can create new applications, or import existing projects or sample applications into the IDE.
-
To establish a project reference between UI application and service application:
- In the Project Explorer view, right-click the UI application.
- Select Properties > Project References.
- Select the check box for the service application or shared library, and click OK.
In the Project Explorer view, a message (with the UI application) appears next to the referenced project name for all the applications you have added to the package.
After packaging the multi-project application, the package consists of the application binary, resource, and data files of the root and referenced applications. Their tizen-manifest.xml files are merged into one. The application ID in the tizen-manifest.xml must be assigned with the package ID as a prefix.
- In the IDE, make sure all the applications you want to include in the package are located in the Project Explorer view.
-
Build and run the UI application.
The service application or shared library is built and run automatically while the UI application is built and run.
| Note |
|---|
| Tizen has limited a multi-project application combination policy for device usability. If you do not follow the policy, the submission of your application to the Tizen Store can be rejected.
For your convenience, some policies can be allowed in the SDK only. For example, you can make a STANDALONE service application or STANDALONE widget application in the IDE, but these applications can be rejected in the Tizen Store. |
The following table shows the possible combinations for a native multi-project. 1 means that only one application can be packaged as a sub application, while M means that multiple applications can be packaged as sub applications. The STANDALONE column defines whether the application can be packaged alone as the main application.
| Main project | Sub project | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STANDALONE | UI | SERVICE | WATCH | WIDGET | IME | |
| UI | Yes | No | M | No | M | No |
| SERVICE | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| WATCH | Yes | No | M | No | No | No |
| WIDGET | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| IME | Yes | M | M | No | No | No |
The following examples illustrate how to read the above table:
- Main UI project alone: Allowed
- Main UI project + 3 service projects packaged together: Allowed
- Main UI project + 1 widget project packaged together: Allowed
- Main service project alone: Not allowed
- Main widget project alone: Not allowed
The following figure illustrates the process of developing a Tizen native application.
Figure: Native application development process