UI Layout: Creating a UI Screen Layout
This tutorial demonstrates how you can compose a UI screen using the layout classes available in the EFL UI component library. It also highlights the capabilities of the EFL layout classes in free style layouting as well as layouting in a particular sequence (such as linear or grid).
This feature is supported in mobile applications only.
Warm-up
Become familiar with the Ecore, Elementary, and Evas API basics by learning about:
-
Creating the UI Layout
Create an application layout.
-
Adding Content to the Screen
Add content to UI screens.
Creating the UI Layout
The sample application uses UI components, such as elm_naviframe and elm_toolbar for the view management, layout classes, such as elm_table, elm_box, and elm_grid for the composition of the screen, and UI components, such as elm_label and elm_image for the content inside the view.
The create_base_gui() function creates the application layout. It starts by creating a window, then adds the elm_conformant component to it to decorate the window with an indicator. It then adds the elm_naviframe component which acts as a view manager for the window and provides the window title functionality. After this it creates the toolbar using the create_toolbar() function and adds it to naviframe.
static void
create_base_gui(appdata_s *ad)
{
Elm_Object_Item *nf_it, *tabbar_it;
// Window
ad->win = elm_win_util_standard_add(PACKAGE, PACKAGE);
elm_win_autodel_set(ad->win, EINA_TRUE);
evas_object_smart_callback_add(ad->win, "delete,request", win_delete_request_cb, NULL);
// Conformant
ad->conform = elm_conformant_add(ad->win);
evas_object_size_hint_weight_set(ad->conform, EVAS_HINT_EXPAND, EVAS_HINT_EXPAND);
elm_win_resize_object_add(ad->win, ad->conform);
evas_object_show(ad->conform);
// Naviframe
ad->nf = elm_naviframe_add(ad->conform);
elm_object_content_set(ad->conform, ad->nf);
evas_object_show(ad->nf);
nf_it = elm_naviframe_item_push(ad->nf, "UiLayout", NULL, NULL, NULL, "tabbar/icon/notitle");
// Tabbar
ad->tabbar = create_toolbar(ad);
elm_object_item_part_content_set(nf_it, "tabbar", ad->tabbar);
// Set the first view
tabbar_it = elm_toolbar_first_item_get(ad->tabbar);
elm_toolbar_item_selected_set(tabbar_it, EINA_TRUE);
// Show the window after the base GUI is set up
evas_object_show(ad->win);
ecore_event_handler_add(ECORE_EVENT_KEY_DOWN, keydown_cb, NULL);
}
The create_toolbar() function creates the toolbar which is then added to the naviframe.
static Evas_Object*
create_toolbar(appdata_s *ad)
{
Evas_Object *tabbar;
tabbar = elm_toolbar_add(ad->nf);
elm_object_style_set(tabbar, "tabbar");
elm_toolbar_shrink_mode_set(tabbar, ELM_TOOLBAR_SHRINK_EXPAND);
elm_toolbar_transverse_expanded_set(tabbar, EINA_TRUE);
elm_toolbar_item_append(tabbar, NULL, "Box", tabbar_item_cb, ad);
elm_toolbar_item_append(tabbar, NULL, "Grid", tabbar_item_cb, ad);
elm_toolbar_item_append(tabbar, NULL, "Table", tabbar_item_cb, ad);
return tabbar;
}
The following figure illustrates the UI Layout.
Figure: UI Layout screen
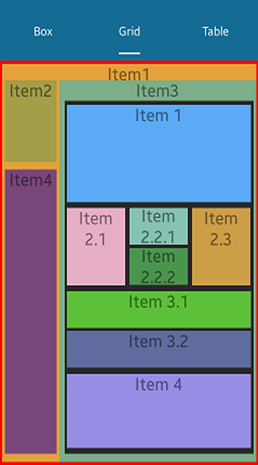
Adding Content to the Screen
The create_box_view() function creates the screen using a recursive composition of the box layout.
static Evas_Object*
create_box_view(Evas_Object *parent)
{
Evas_Object *box, *box1, *box2, *box3;
box = elm_box_add(parent);
elm_box_padding_set(box, 10, 10);
evas_object_size_hint_weight_set(box, EVAS_HINT_EXPAND, EVAS_HINT_EXPAND);
evas_object_size_hint_align_set(box, EVAS_HINT_FILL, EVAS_HINT_FILL);
box1 = elm_box_add(box);
elm_box_horizontal_set(box1, EINA_TRUE);
elm_box_padding_set(box1, 8, 8);
evas_object_size_hint_weight_set(box1, EVAS_HINT_EXPAND, EVAS_HINT_EXPAND);
evas_object_size_hint_align_set(box1, EVAS_HINT_FILL, EVAS_HINT_FILL);
evas_object_show(box1);
box2 = elm_box_add(box);
elm_box_padding_set(box2, 6, 6);
evas_object_size_hint_weight_set(box2, EVAS_HINT_EXPAND, EVAS_HINT_EXPAND);
evas_object_size_hint_align_set(box2, EVAS_HINT_FILL, EVAS_HINT_FILL);
evas_object_show(box2);
box3 = elm_box_add(box);
elm_box_padding_set(box3, 5, 5);
evas_object_size_hint_weight_set(box3, EVAS_HINT_EXPAND, EVAS_HINT_EXPAND);
evas_object_size_hint_align_set(box3, EVAS_HINT_FILL, EVAS_HINT_FILL);
elm_box_homogeneous_set(box3, EINA_FALSE);
evas_object_show(box3);
}
Once the box layout is created, content or another box layout is added to the box. Box implements the size policy during the size calculation.
// Add an item to the box Evas_Object *item1 = create_content(box, "Item 1"); evas_object_size_hint_min_set(item1, 0, 40); elm_box_pack_end(box, item1); elm_box_pack_end(box, box1); elm_box_pack_end(box, box3); elm_box_pack_end(box, create_content(box, "Item 4")); // Add an item to the box1 elm_box_pack_end(box1, create_content(box1, "Item 2.1")); elm_box_pack_end(box1, box2); elm_box_pack_end(box1, create_content(box1, "Item 2.3")); // Add an item to the box2 elm_box_pack_end(box2, create_content(box2, "Item 2.2.1")); elm_box_pack_end(box2, create_content(box2, "Item 2.2.2")); // Add an item to the box3 elm_box_pack_end(box3, create_content(box3, "Item 3.1")); elm_box_pack_end(box3, create_content(box3, "Item 3.2"));
The create_table_view() function creates the screen by composing table layout with content and grid view.
static Evas_Object*
create_table_view(Evas_Object *parent)
{
Evas_Object *table, *item;
table = elm_table_add(parent);
elm_table_padding_set(table, 10, 10);
elm_table_homogeneous_set(table, EINA_TRUE);
evas_object_size_hint_weight_set(table, EVAS_HINT_EXPAND, EVAS_HINT_EXPAND);
evas_object_size_hint_align_set(table, EVAS_HINT_FILL, EVAS_HINT_FILL);
item = create_content(table, "Item 1");
elm_table_pack(table, item, 0, 0, 2, 1);
item = create_content(table, "Item 2");
elm_table_pack(table, item, 2, 0, 1, 1);
item = create_content(table, "Item 3");
elm_table_pack(table, item, 0, 1, 3, 1);
// Add a grid view item
item = create_grid_view(table);
evas_object_show(item);
elm_table_pack(table, item, 0, 2, 3, 10);
return table;
}
The table layout can be used for freestyle layouting, and for standard layouts, such as lists and grids. It does not consider the size policy of the child item during size calculation.
The create_grid_view() function composes a screen using the grid layout and also uses box and table layout as a child item to pack inside a grid. It uses free style layouting, and during size evaluation of the child item, it does not take the size policy of the child item into consideration.
static Evas_Object*
create_grid_view(Evas_Object *parent)
{
Evas_Object *grid, *item;
grid = elm_grid_add(parent);
evas_object_size_hint_weight_set(grid, EVAS_HINT_EXPAND, EVAS_HINT_EXPAND);
evas_object_size_hint_align_set(grid, EVAS_HINT_FILL, EVAS_HINT_FILL);
// Red background for the grid
item = create_bg(grid, 255, 0, 0);
elm_grid_pack(grid, item, 0, 0, 100, 100);
// Add the item to the grid
item = create_content(grid, "Item1");
elm_grid_pack(grid, item, 1, 1, 98, 98);
item = create_content(grid, "Item2");
elm_grid_pack(grid, item, 2, 5, 20, 20);
item = create_content(grid, "Item3");
elm_grid_pack(grid, item, 23, 5, 76, 94);
item = create_content(grid, "Item4");
elm_grid_pack(grid, item, 2, 27, 20, 70);
// Black background for the box view item
item = create_bg(grid, 40, 40, 40);
elm_grid_pack(grid, item, 25, 10, 73, 87);
// Add the box view item to the grid
item = create_box_view(grid);
evas_object_show(item);
elm_grid_pack(grid, item, 26, 11, 71, 85);
return grid;
}

