SensorBall Overview
Sensor Ball is an application that simulates behavior of the ball in three different environments.
The application reads the accelerometer values of the device and changes the position of the ball to simulate inertia and gravity forces. The user can impact the movement of the ball by changing the orientation of the device.
For information on creating the sample application project in the IDE, see Creating Web Sample Applications, and on the coding of the sample application, see Sensor Ball task.
The following figure illustrates the main screen of the SensorBall.
Figure: SensorBall screen
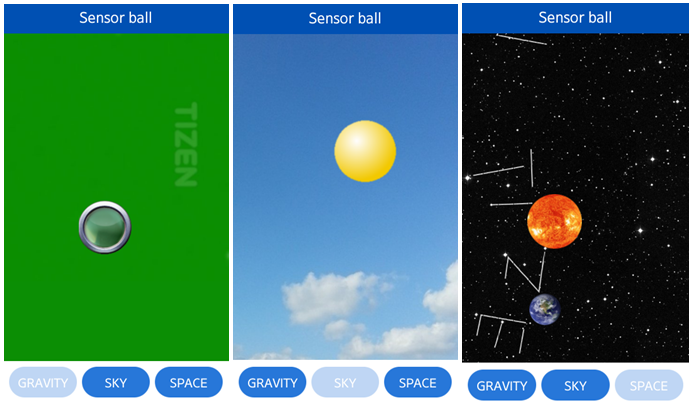
The main page of the application contains the scene and three buttons at the bottom. The buttons allow switching between the following environments: gravity, sky, and space.
The gravity environment simulates a ball in indoor conditions. The movement of the ball is affected by gravity. The screenshot on the left presents the scene with this environment.
The sky environment simulates a balloon in the sky. The balloon is filled with gas lighter than air, so it slowly moves up. The screenshot in the middle presents the scene.
-
The space environment simulates a planet in space. Sun and Earth are placed on the scene and Earth orbits the sun as shown in the screenshot on the right.
Source Files
You can create and view the sample application project including the source files in the IDE.
| File name | Description |
|---|---|
| config.xml | This file contains the application information for the platform to install and launch the application, including the view mode and the icon to be used in the device menu. |
| index.html | This is a starting file from which the application starts loading. It contains the layout of the application screens. |
| js/ | This file contains the application code. |
| js/core/ | This file contains the core library. |
| js/models/ball.js | This file is the model of the ball. It contains position and speed of the ball. |
| js/models/gravity.js | This file is the model of the gravity. It performs calculations for the ball and the gravity. |
| js/models/space.js | This file is the model of space. It performs calculations for the planet in space. |
| js/models/sky.js | This file is the model of the sky. It performs calculations for the balloon in the sky. |
| js/views/ | This file contains the code to render the elements of the scene and handle the UI events. |
| js/app.js | This file defines an initialization module. |
| images/ | This directory contains the images used to create the user interface. |
| css/ | This directory contains the CSS styling for the application UI. |
Implementation
The following functions demonstrate adding a devicemotion event listener and handling the event.
/* views/main.js */
function bindEvents()
{
window.addEventListener('tizenhwkey', onHardwareKeysTap);
window.addEventListener('devicemotion', onDeviceMotion);
document.addEventListener('webkitvisibilitychange', onVisibilityChange);
$('#' + GRAVITY_BUTTON_ID).on('tap', function onBallTap()
{
startGravity();
});
$('#' + SKY_BUTTON_ID).on('tap', function onSkyTap()
{
startSky();
});
$('#' + SPACE_BUTTON_ID).on('tap', function onSpaceTap()
{
startSpace();
});
}
The following function sets the motion data to the given event value.
/* models/ball.js */
function setMotionData(event)
{
motionData = event;
}
The following function calculates the velocity of the ball based on the motion data.
/* models/gravity.js */
function calculateGravityBallPosition()
{
var x = 0,
y = 0,
ddx = 0,
ddy = 0;
if (motionData !== null)
{
x = -motionData.accelerationIncludingGravity.x;
y = -motionData.accelerationIncludingGravity.y;
}
ddx = x * -cdd;
ddy = y * cdd;
dX += ddx;
dY += ddy;
dX *= resistance;
dY *= resistance;
ballX += dX;
ballY += dY;
}
The following function calculates the position of the Sun in the space mode based on the data received from the motion sensor.
/* models/space.js */
function getSunPosition()
{
var result = {},
x = -motionData.accelerationIncludingGravity.x,
y = -motionData.accelerationIncludingGravity.y,
rX = -8.0,
rY = -8.0,
cX = (gameWidth - sunWidth) / 2,
cY = (gameHeight - sunHeight) / 2,
tX = cX + (-x * rX),
tY = cY + (y * rY),
bdX = tX - sunX,
bdY = tY - sunY,
br = 0.2;
sunX += bdX * br;
sunY += bdY * br;
result.x = sunX;
result.y = sunY;
return result;
}
The following function calculates the position of the background in the space mode based on the data received from the motion sensor.
/* models/space.js */
function getBackgroundPosition()
{
var result = {},
x = -motionData.accelerationIncludingGravity.x,
y = -motionData.accelerationIncludingGravity.y,
rX = -30.0,
rY = -30.0,
cX = (gameWidth - backgroundWidth) / 2,
cY = (gameHeight - backgroundHeight) / 2,
tX = cX + (-x * rX),
tY = cY + (y * rY),
bdX = tX - backgroundLeft,
bdY = tY - backgroundTop,
br = 0.2;
backgroundLeft += bdX * br;
backgroundTop += bdY * br;
result.left = backgroundLeft;
result.top = backgroundTop;
return result;
}

