Using the Extended Emulator Features
The Emulator features can be extended in many ways. With the Emulator, you can:
- Use multi-point touch
- Share a directory
- Use a Webcam
- Use network features
- Use custom skin layout
- Use EventCast
- Use Emulator start-up options
You can also familiarize yourself with the Emulator directory structure.
Using Multi-point Touch
To create a multi-point touch effect in the Emulator, press and hold the CTRL key (Command key in Mac OS® X), while mouse-clicking on the Emulator screen.
Adding a Touch Point
To add a touch point on the Emulator screen, press and hold the CTRL key (Command key in Mac OS® X) and mouse-click a point on the screen.
You can add touch points up to the maximum amount of multi-point touches. To get the maximum amount, use the System::SystemInfo::GetValue() method with the MultiPointTouchCount key.
Figure: Adding a touch point

Moving an Existing Point
To move an existing point one by one, press and hold the CTRL key (Command key in Mac OS® X), mouse-click an existing point, and move it to another location on the screen.
Figure: Moving an existing point
To move all existing points together, press and hold the CTRL (Command in Mac OS® X) and SHIFT keys, mouse-click an existing point, and move it to another location on the screen.
Figure: Moving all existing points
To move 2 existing points symmetrically together, press and hold the CTRL (Command in Mac OS® X) and ALT keys, mouse-click an existing point, and move it to another location on the screen.
Figure: Symmetrically moving 2 existing points
Ending the Multi-point Touch
To end the multi-point touch, release the CTRL key (Command key in Mac OS® X). The touched points on the Emulator screen are invalidated, and the next screen touch event is read as a new event, not part of the previous multi-point touch event.
Figure: Invalidating touched points

Sharing a Directory
You are able to share a directory between Emulator and your computer. The host machine's directory is shown as /mnt/host in the Emulator.
- Run the Emulator Manager and click Create New or Modify.
- In the File Sharing section of the VM property, enable the Sharing button and select a directory to share.
- Start the Emulator.
You can also add a shared directory in the Emulator Control Panel:
- Start the Emulator.
- Right-click the Emulator and select Control Panel .
- Move to the Host Directory Sharing tab.
- Mount or unmount the host machine directory.
| Note |
|---|
| You must have a read/write permission for the directory you want to share. You can share only one directory. |
Using a Webcam
With the Emulator, you can host a Webcam just like a device camera.
Before running the application, install a USB-connected Webcam or embedded Webcam on your machine. On Linux, the Webcam feature uses libv4l-0. If you do not have it on your machine, this feature does not work properly. You can check the feature status with the following command:
$ dpkg -l | grep libv4l-0
| Note |
|---|
|
The following table lists the host Webcam features.
| Feature | Detail | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| FPS | 30 fps | - |
| Preview image format | YUYV I420 YV12 |
- |
| Capture image format | YUYV I420 YV12 JPEG |
- |
| Preview resolution | QSIF: 160 x 120 QCIF: 176 x 144 QVGA: 320 x 240 CIF: 352 x 288 VGA: 640 x 480 |
- |
| Capture resolution | QSIF: 160 x 120 QCIF: 176 x 144 QVGA: 320 x 240 CIF: 352 x 288 VGA: 640 x 480 |
- |
| Attributes | Brightness Contrast |
Unsupported attributes can return an error. For example, the camera_start_focusing() method returns an error. |
Using Emulator in a Network
The Tizen Emulator is based on the QEMU virtual machine, and uses QEMU user networking (SLIRP), which is the default networking backend and generally the easiest to use. The Emulator supports TCP and UDP, and "ping" within a guest (QEMU is patched for ping to work; however, raw socket is not supported). For more information, see QEMU Networking documentation.
The Emulator provides a sub-network, such as the following:
- 10.0.2.2: Gateway, host machine
- 10.0.2.3: DNS (you can specify the Emulator to use the host DNS IP when the Emulator starts)
- 10.0.2.16: Guest OS IP (different from QEMU's default setting of 10.0.2.15)
Figure: Emulator network architecture
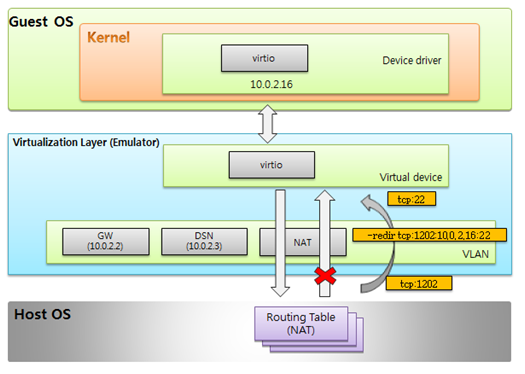
Network Connections
The Emulator provides the following network connection solutions (external to internal):- Guest to External: Connection available
- External to Guest: Port redirection required when starting to boot
The QEMU redirection option can be appended in the <TIZEN_SDK_DATA>/emulator/vms/<image name>/vm_config.xml file with the following appending command:
-redir <PROTOCOL>:<HOST_PORT>:10.0.2.16:<GUEST_PORT>
Note that <PROTOCOL> supports only udp and tcp in the <advancedOptions> section:
<usability> <logging> <level>NONE</level> </logging> <fileSharing/> <hwVirtualization>true</hwVirtualization> <advancedOptions>-redir tcp:1202:10.0.2.16:22</advancedOptions> </usability>
You can also connect one Emulator instance with another by using redirection. To set up redirection (where A and B are Emulator instances):
- Set up the server on A, listening to 10.0.2.16:<ServerPort>.
- On A, append the -redir tcp:<B's localPort>:10.0.2.16:<A's serverPort> redirection option in the vm_config.xml file.
- On B, let the client connect to 10.0.2.2:<B's localPort>.
For more information, see How to use Network.
Proxy Configuration
The Tizen Emulator uses a host network proxy when connecting to the Internet.
Direct Internet and manual proxy configuration are supported, but the following preallocated addresses are not supported as a manual proxy:
- Localhost
- 127.0.0.0/8
- 10.0.0.0/16
The automatic proxy configuration is not supported, due to license issues.
Using Custom Skin Layout
An Emulator skin comprises an XML meta file, which defines layout-related information, such as skin image file name, display location, and the location of hardware keys. This file is located in <TIZEN_SDK>/platform/<PROFILE_NAME>/emulator-resources/skins/<SKIN_NAME>/default.dbi.
The following example shows the contents of the default.dbi layout file:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <EmulatorUI xmlns="http://www.tizen.org/emulator/skin/dbi" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"> <dbi version="2.0"/> <rotations> <!--Skin mode definition--> <rotation name="Portrait"> <!--Display number of identification--> <display id="0">"> <!--Display screen size and position--> <region left="35" top="86" width="480" height="800"/> </display> <imageList> <!--Resource file name of the usual skin image--> <mainImage>default_0.png</mainImage>"> <!--Resource file name of the skin image when HW key events occur--> <keyPressedImage>default_0_p.png</keyPressedImage> </imageList> <keyMapList> <keyMap> <!--Optional--> <!--HW key region size and position--> <region left="238" top="887" width="74" height="74"/> <eventInfo> <keyCode>139</keyCode> <!--Keycode value--> <keyName>HOME</keyName> <!--HW key name--> </eventInfo> <!--This line to be displayed when mouse hovers over the HW key region--> <tooltip>Home</tooltip> </keyMap> </keyMapList> </rotation> </rotations> <hover> <!--RGB color of the HW key hover--> <color B="255" G="255" R="255" /> </hover> </EmulatorUI>
The Emulator skin also comprises a property file, which defines skin-related information, such as skin name and supported resolutions. This file is located in <TIZEN_SDK>/tools/emulator/skins/<SKIN_NAME>/info.ini.
The following example shows the contents of the info.ini property file:
skin.name=Phone 480x800 resolution.width=480 resolution.height=800
To create your own skin layout:
- Create a new skin folder in the <TIZEN_SDK>/tools/emulator/skins/ folder.
- In the skin folder, define the contents of the default.dbi and info.ini files and include the required skin image files.
-
Select the skin name in the Emulator Manager. You can also use the Emulator start-up options in the command line.
The image defined in your modified XML meta file is displayed when the Emulator is launched.
| Note |
|---|
| If you re-install the Tizen IDE, the custom skin folders are reset. |
Using EventCast
The Emulator supports event injection using ECP (Emulator Control Panel). However, injecting sensor events using ECP is less intuitive and convenient. When you are injecting events, touching the Emulator screen simultaneously is impossible. EventCast enables you to inject sensor and touch events more intuitively using a real target device.
The following figure illustrated how the EventCast application in the target device gathers events and passes them to the Emulator controller, which converts and hands them over to the Tizen platform. This is convenient in case you do not have a Tizen mobile device.
Figure: EventCast architecture
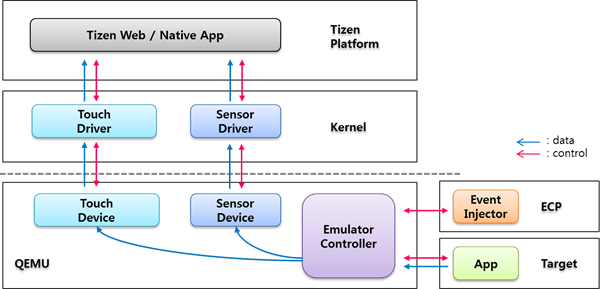
EventCast provides the following features:
- Touch: Maximum number of touch points is 10
- Sensors: Accelerometer, gyroscope, geo-magnetic, proximity, light sensors
- Display: Getting images of the Tizen Emulator and drawing them when using touch features
Prerequisites
When connecting through USB, ADB is required to make a connection. If you have already installed Android SDK on the PC, ADB is located at a <installed Android SDK>/sdk/platform-tools directory. Otherwise, you can download only ADB or install Android SDK.
To install ADB:
-
Ubuntu/Mac OS® X: Download ADB and then install it in the /usr/bin directory.
For more information, see http://code.google.com/p/adb-fastboot-install/.
-
Download ADB and install it in the C:\ADB directory.
For more information, see http://rubenalamina.mx/custom-installers/android-adb-fastboot/.
When connecting through Wi-Fi, make sure that your android device and PC are within the same AP.
Installing EventCaster
EventCaster is the application on the target device. It communicates with the Tizen Emulator through the TCP/IP protocol. It can connect to the Emulator using USB or Wi-Fi.
You can install the EventCaster from Google Play(https://github.com/eventcaster/eventcaster.git) and install it manually.
Connecting EventCaster to the Emulator
To connect the EventCaster application to the Emulator:
- Connect through USB:
- Locate the developer options
On most devices running Android 3.2 or older, you can find the option under Settings > Applications > Development.
On Android 4.0 and newer, it is in Settings > Developer options.
Note On Android 4.2 and newer, the developer options are hidden by default. To make them available, go to Settings > About phone and tap Build number seven times. Return to the previous screen to find the developer options. - Enable USB debugging.
- Connect the device to a computer through USB.
- Launch the EventCaster.
- Start the server using default port (7000) or enter the port number.
- Forward a TCP port using the adb forward command.
For example, you can forward the 7000 port in the application to the 1234 port in your computer: adb forward tcp:1234 tcp:7000
- Launch the Tizen Emulator and the Emulator Control Panel (ECP) in the Emulator context menu.
- Select the USB checkbox on the EventCast tab of the Emulator Control Panel.
- Enter the forwarded port number and click Connection on the ECP.
If the Emulator connects to app successfully, the Show Event button in the application is activated.
- Click Show Event. You can now inject a sensor or touch value to the Emulator.
- Locate the developer options
- Connect through Wi-Fi:
- Enable Wi-Fi on device and select the Wi-Fi network.
- Connect the Android device to a network where you also have a computer running the Emulator.
- Launch EventCaster and click Read WiFi.
The application gets the IP address of the connected network.
- Choose Start Server button.
- Select the Wi-Fi checkbox on the EventCast tab of the Emulator Control Panel.
- Enter the IP address and port number using EventCaster and then click Connect on the Emulator Control Panel.
If the Emulator connects to the application successfully, the Show Event button in the application is activated.
- Click Show Event. You can now inject a sensor or touch value to the Emulator.
Using Emulator Start-up Options
You can launch the Emulator with specific settings by defining start-up options in the command line:
# ./emulator-x86 --skin-args <skin options> --qemu-args <QEMU options>
The Emulator binaries are located in the <TIZEN_SDK>/tools/emulator/bin directory. The Tizen Emulator provides 2 types of start-up options that you can set: skin options (such as width and height) and QEMU options (such as network and memory).
The following tables list the available options.
| Category | Option | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resolution | width=x | Yes | This option makes the Emulator use a specific skin image width. The width value must be one of the video resolutions that the Emulator can support. |
| height=x | Yes | This option makes the Emulator use a specific skin image height. The height value must be one of the video resolutions that the Emulator can support. | |
| Heartbeat | hb.ignore=x | No | This option is used to activate the Emulator debugging mode. Generally, a skin process for the Emulator periodically checks the heartbeat that an Emulator process sends. When the Emulator is in the debugging mode using gdb, the skin process is terminated automatically, because the Emulator cannot send a heartbeat to the skin process. In that case, you can set the hb.ignore option as true to debug the Emulator. If this option is true, the skin process does not check the heartbeat that the Emulator sends. The default value of this option is false. |
| Skin image file path | skin.path=xxx | Yes | Emulator loads the skin image files in this path. If this option is omitted, the Emulator finds the image files in the installed 'skins' directory. |
| Category | Option | Description |
|---|---|---|
| File system image | -drive file=<IMAGE_PATH>/emulimg.x86 | Sets an image path to the file to be used as a drive image. |
| Swap file system image | -drive file=<SWAP_IMAGE_PATH>/swap.img | Sets a swap image path to the file to be used as a swap image. |
| Network | -net user | Uses the user mode network stack, which requires no administrator privilege to run. |
| -net nic,model=virtio,macaddr=<MAC_ADDRESS> | Creates a new network interface card and connects it to VIRTIO. <MAC_ADDRESS> is recorded in <TIZEN_SDK_DATA>/emulator/vms/.tizen-em-info. For example: E8:11:32:33:38:81 | |
| USB | -usb | Enables the USB driver. |
| TouchScreen | -device virtio-touchscreen-pci | Uses the Maru Touchscreen device for display. |
| Kernel | -kernel <KERNEL_PATH> | Uses bzImage as the kernel image. |
| BIOS | -vga none | Sets the VGA card. |
| -L <BIOS_PATH> | Sets the directory for the BIOS, VGA BIOS, and key maps. | |
| Time | -rtc base=utc | Sets the real time clock with UTC. |
| KVM (in Ubuntu®) | -enable-kvm | Enables KVM (hardware virtualization support). |
| HAX (in Windows® or Mac OS® X) | -enable-hax | Enables HAX (hardware virtualization support). |
| SMP | -smp <NUMBER OF CPUs> | Sets the number of CPUs. |
| Boot order | -boot c | Sets the boot order of the Emulator. The letter c indicates a hard disk. |
| Kernel parameters | -append<parameters> | Sets the kernel command line parameters from the Emulator to the kernel. |
| Kernel log | -serial file:<LOG_PATH>/emulator.klog | Writes the kernel log into the <LOG_PATH>/emulator.klog file. |
| Memory | -m <MEMORY_SIZE> | Sets the memory size in the Tizen platform to, for example, 512 or 1024. |
| Board | -M maru-x86-machine | Sets the Emulator machine as maru-x86-machine. |
| Video card | -enable-vigs | Enables VIGS (Virtualized Graphics System) as the video card. |
| -vigs-backend <VIGS_BACKEND> | Sets the back end as sw or gl (software or OpenGL®). | |
| GPU support | -enable-yagl | Enables host GL acceleration. |
| -yagl-backend <YAGL_BACKEND> | Sets the back end as vigs or offscreen. | |
| Sound | -soundhw all | Enables all sound cards. |
| Display booting status | -device virtio-esm-pci | Sets the display booting status of the Emulator. |
| Codec | -device codec-pci | Enables codec devices. |
| Hardware key | -device virtio-hwkey-pci | Enables hardware keys. |
| Host keyboard | -device virtio-keyboard-pci | Enables host keyboards. |
| Rotary | -device virtio-rotary-pci | Enables a rotary device. |
| Brightness | -device maru-brightness | Enables the brightness control. |
| Camera | -device maru-camera | Enables the host Webcam support. |
| Power | -device virtio-power-pci | Enables the battery. |
| Jack | -device virtio-jack-pci,jacks=<Jack types> | Enables jack devices. Supported jacks are USB, ear jack, ear key, HDMI, and charger. The ampersand ('&') symbol is used for multiple jacks. |
| Emulator virtual device interface | -device virtio-evdi-pci | Enables the common interface between the Emulator daemon on the guest side and the Emulator on the host side.
To use the Emulator Control Panel, this option is required. |
| Sensors | -device virtio-sensor-pci,sensors=<Sensor types> | Enables sensor devices. Supported sensors are accelerometer, gyroscope, geomagnetic, light, proximity, haptic, pressure, ultraviolet, and heart rate monitor.
The names of sensor types are accel, gyro, geo, light, proxy, haptic, press, uv, and hrm, respectively. The ampersand ('&') symbol is used for multiple sensor support. |
| Vmodem | -device virtio-vmodem-pci | Enables the Virtual Modem. |
The following command is an example of using the Emulator start-up options:
- Mobile
<TIZEN_SDK>/tools/emulator/bin/emulator-x86.exe --skin-args width=480 height=800 skin.path= <TIZEN_SDK>/platforms/<PROFILE_NAME>/emulator-resources/skins/<SKIN_NAME> --qemu-args -drive file= <TIZEN_SDK_DATA>/emulator/vms/<VM_NAME>/emulimg-<VM_NAME>.x86,if=virtio,index=1 -boot c -append "console=ttyS0 video=LVDS-1:480x800-32@60 dpi=2330 ip=10.0.2.16::10.0.2.2:255.255.255.0::eth0:none vm_name=<VM_NAME>" -serial file: <TIZEN_SDK_ DATA >/emulator/vms/<VM_NAME>/logs/emulator.klog -m 512 -M maru-x86-machine -net nic,model=virtio,macaddr=<MAC_ADDRESS> -soundhw all -usb -vga none -enable-vigs -L <TIZEN_SDK>/tools/emulator/data/bios -kernel <TIZEN_SDK>/tools/emulator/data/kernel/bzImage.x86 -net user,dhcpstart=10.0.2.16 -rtc base=utc -drive file= <TIZEN_SDK_DATA>/emulator/vms/<VM_NAME>/swap-<VM_NAME>.img,if=virtio, index=2 -enable-hax -vigs-backend gl -enable-yagl -yagl-backend vigs -device virtio-esm-pci -device virtio-hwkey-pci -device virtio-keyboard-pci -device virtio-evdi-pci -device virtio-sensor-pci,sensors=accel&geo&gyro&light&proxi& haptic&press&uv&hrm -device virtio-power-pci -device virtio-jack-pci,jacks=earjack&charger&usb -device codec-pci -device maru-brightness -device virtio-vmodem-pci -device maru-camera -device virtio-touchscreen-pci,max_point=10
- Wearable
<TIZEN_SDK>/tools/emulator/bin/emulator-x86.exe --skin-args width=360 height=360 skin.path= <TIZEN_SDK>/platforms/<PROFILE_NAME>/emulator-resources/skins/<SKIN_NAME> --qemu-args -drive file= <TIZEN_SDK_DATA>/emulator/vms/ <VM_NAME>/emulimg-<VM_NAME>.x86,if=virtio,index=1 -boot c -append "console=ttyS0 video=LVDS-1:360x360-32@60 dpi=302 ip=10.0.2.16::10.0.2.2:255.255.255.0::eth0:none vm_name=<VM_NAME>" -serial file: <TIZEN_SDK_DATA>/emulator/vms/<VM_NAME>/logs/emulator.klog -m 512 -M maru-x86-machine -net nic,model=virtio,macaddr=<MAC_ADDRESS> -soundhw all -usb -vga none -enable-vigs -L <TIZEN_SDK>/tools/emulator/data/bios -kernel <TIZEN_SDK>/tools/emulator/data/kernel/bzImage.x86 -net user,dhcpstart=10.0.2.16 -rtc base=utc -drive file= <TIZEN_SDK_DATA>/emulator/vms/<VM_NAME>/swap-<VM_NAME>.img,if=virtio,index=2 -enable-hax -vigs-backend gl -enable-yagl -yagl-backend vigs -device virtio-esm-pci -device virtio-hwkey-pci -device virtio-evdi-pci -device virtio-sensor-pci, sensors=accel&geo&gyro&light&proxi&haptic&press&uv&hrm -device virtio-power-pci -device virtio-jack-pci,jacks=charger&usb -device codec-pci -device maru-brightness -device virtio-vmodem-pci -device maru-camera -device virtio-touchscreen-pci,max_point=2 -device virtio-rotary-pci
Emulator Directory Structure
The following table describes the content of the Emulator directory, located in the <TIZEN_SDK>/tools/emulator folder.
| Folder or file | Description |
|---|---|
| bin/ | Binary files |
| bin/emulator-control-panel.jar | Emulator Control Panel |
| bin/emulator-control-panel-cli.jar | Emulator Control Panel CLI (Command Line Interface) |
| bin/emulator-manager | Emulator manager binary to launch the emulator-manager.jar file |
| bin/emulator-manager.jar | Emulator manager jar, which can also launch the Emulator with the Emulator Manager. |
| bin/em-cli | Emulator manager CLI (Command Line Interface) |
| bin/emulator-skin.jar | Emulator skin |
| bin/emulator-x86 | x86 Emulator binary, including QEMU |
| bin/protobuf.jar | Protocol buffer library |
| bin/libecp.jar | profile independent library for ECP |
| bin/swt.jar | SWT library |
| bin/jna-<version>.jar | JNA library |
| data/bios/ | .bin files for initializing the guest OS |
| data/kernel/ | Kernel image for the guest Linux OS |
| storages/sdcard/sdcard_xxx.img | .img files (base sdcard images) specific to the data size used by the Emulator Manager |
| storages/swap/swap.img | Disk image for swap |
The following table describes the platform directories that are located in the <TIZEN_SDK>/platform/<Profile>-<VERSION>/emulator-images folder.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| x86-standard/ | Platform directory |
| x86-standard/emuling-<VERSION>.x86 | Base image, which represents an Emulator root file system for x86 in the guest OS view |
| x86-standard/info.ini | File for specifying information of the Emulator disk image |
The following table describes the platform directories that are located in the <TIZEN_SDK>/platforms/<Profile>-<VERSION>/emulator-resources folder.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| plugins/ | Plugins for profile |
| plugins/ecp-plugin.jar | Plugin for the Emulator Control Panel |
| plugins/ecp-plugin.xml | XML file for the ecp-plugin.jar file configuration |
| plugins/em-plugin.jar | Plugin for the Emulator Manager |
| skins/ | Emulator skin images specific to the Emulator resolution, and icons for the Emulator option button and shortcut |
| skins/<skin name>/default.dbi | Metafile for the Emulator skin layout |
| skins/<skin name>/info.ini | File for specifying Emulator skin information |
| template/<image name>.xml | XML file for default configuration of the virtual machine created by the Emulator Manage |
| template/<image name>-template.xml | XML file for the template of the virtual machine created by the Emulator Manager |
The following table describes the directory structure of the user-specific files that are located in the <TIZEN_SDK_DATA>/emulator/vms folder.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| emulator-manager.log | Emulator Manager log file |
| last-created_<PROFILE>-<VERSION>_<image name>.xml | This file saves properties of VM that user created last. And when user create new VM next time, properties in this file is displayed as default |
| .em.lock | This lock file is used for synchronization between VM operation like modify, delete, launch |
| .tizen-em-info | Configuration file for Emulator Manager |
| <image name>/ | Target-specific images |
| <image name>/.skin.properties | Hidden data for the Emulator skin |
| <image name>/emulimg-<image name>.x86 | Writable <image name> image file |
| <image name>/swap-<image name>.img | Swap image file |
| <image name>/vm_config.xml | Hardware configuration (for more information, see Virtual Machine) |
| <image name>/${USER}.lock | This lock file is used for synchronization between VM and Emulator Control Panel to set/get operations |
| <image name>/logs/ | Log files (Emulator, kernel, emulator-skin log) |


