CSS Text Module (Level 3): Manipulating Text
You can apply various text effects easily.
The new text features in CSS Text Module Level 3 include:
- Text properties
You can use CSS text properties, such as text-transform, text-align, text-indent, letter-spacing, and word-spacing, to manipulate and transform text.
Manipulating Text
To enhance the user experience of your application, you must learn to handle line breaking, justification, alignment, white space handling, and text transformations using CSS text properties:
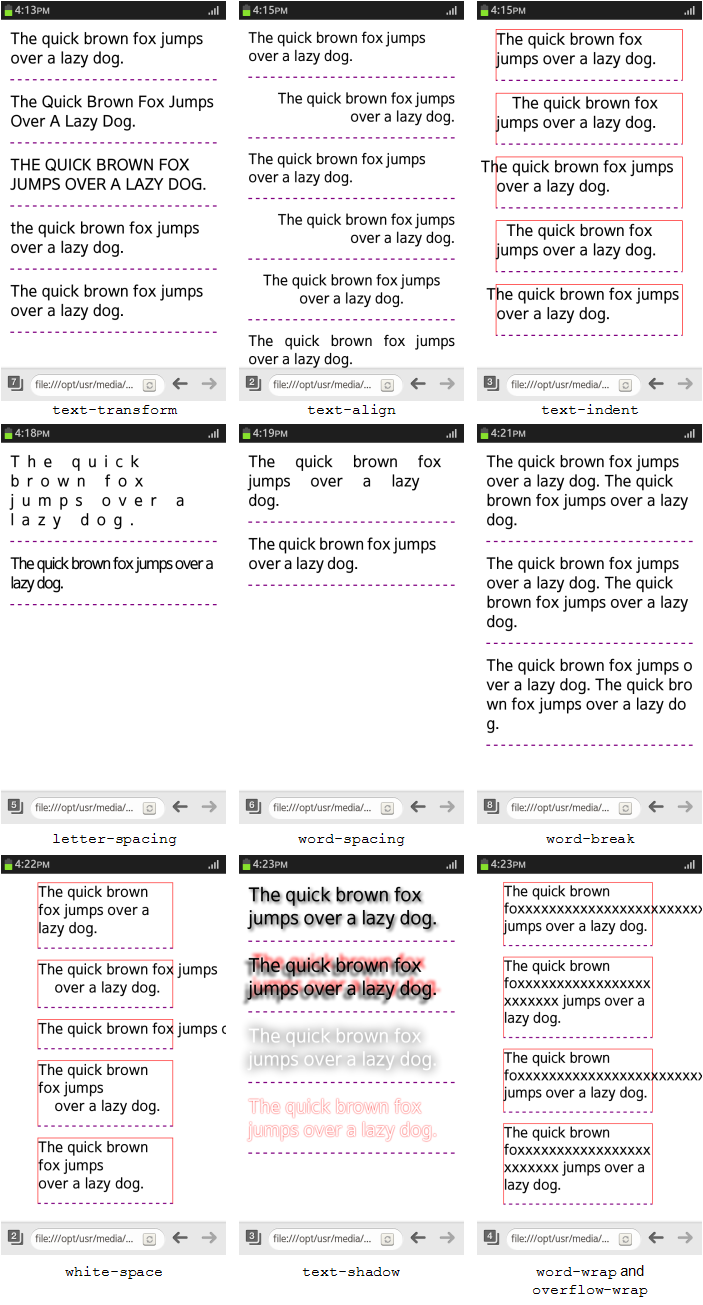
- Define the text-transform property within a <style> element in the <head> section of the Web page to control the text capitalization:
<head> <style> p:nth-child(1) {text-transform: none;} p:nth-child(2) {text-transform: capitalize;} p:nth-child(3) {text-transform: uppercase;} p:nth-child(4) {text-transform: lowercase;} p:nth-child(5) {text-transform: full-width;} </style> </head> <body> <p>The quick brown fox jumps over a lazy dog.</p> <p>The quick brown fox jumps over a lazy dog.</p> <p>The quick brown fox jumps over a lazy dog.</p> <p>The quick brown fox jumps over a lazy dog.</p> <p>The quick brown fox jumps over a lazy dog.</p> </body> - Define the text-align property, which controls the text alignment:
<head> <style> p:nth-child(1) {text-align: start;} p:nth-child(2) {text-align: end;} p:nth-child(3) {text-align: left;} p:nth-child(4) {text-align: right;} p:nth-child(5) {text-align: center;} p:nth-child(6) {text-align: justify;} </style> </head> - Define the text-indent property, which controls the text indentation:
<head> <style> p:nth-child(1) {text-indent: 0} p:nth-child(2) {text-indent: 1em} p:nth-child(3) {text-indent: -1em} p:nth-child(4) {text-indent: 5%} p:nth-child(5) {text-indent: -5%} </style> </head> - Define the letter-spacing property, which controls the letter spacing:
<head> <style> p:nth-child(1) {letter-spacing: .5em} p:nth-child(2) {letter-spacing: -.1em} </style> </head> - Define the word-spacing property, which controls the space between words:
<head> <style> p:nth-child(1) {word-spacing: 1em} p:nth-child(2) {word-spacing: -.1em} </style> </head> - Define the word-break property, which determines the line breaking rules for non-CJK (Chinese, Japanese, and Korean) scripts:
<head> <style> p:nth-child(1) {word-break: normal} p:nth-child(2) {word-break: keep-all} p:nth-child(3) {word-break: break-all} </style> </head> - Define the white-space property, which determines the handling of empty space within an element:
<head> <style> p:nth-child(1) {white-space: normal} p:nth-child(2) {white-space: pre} p:nth-child(3) {white-space: nowrap} p:nth-child(4) {white-space: pre-wrap} p:nth-child(5) {white-space: pre-line} </style> </head> <body> <p>The quick brown fox jumps over a lazy dog.</p> <p>The quick brown fox jumps over a lazy dog.</p> <p>The quick brown fox jumps over a lazy dog.</p> <p>The quick brown fox jumps over a lazy dog.</p> <p>The quick brown fox jumps over a lazy dog.</p> </body> </html> - Define the text-shadow property, which adds a shadow effect to text:
<head> <style> p:nth-child(1) {text-shadow: 0.1em 0.1em 0.2em rgba(0, 0, 0, .7)} p:nth-child(2) {text-shadow: -0.2em 0.2em 0.2em #000, 0.2em -0.2em 0.2em #f00} p:nth-child(3) {color: #fff; text-shadow: 0 0 .7em #000;} p:nth-child(4) {color: #fff; text-shadow: 0 0 1px #f00;} </style> </head> - Define the word-wrap and overflow-wrap properties, which control forced line breaks when the length of a word is longer than the area where it is displayed:
<head> <style> p:nth-child(1) {word-wrap: normal} p:nth-child(2) {word-wrap: break-word} p:nth-child(3) {overflow-wrap: normal} p:nth-child(4) {overflow-wrap: break-word} </style> </head> <body> <p>The quick brown foxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx jumps over a lazy dog.</p> <p>The quick brown foxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx jumps over a lazy dog.</p> <p>The quick brown foxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx jumps over a lazy dog.</p> <p>The quick brown foxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx jumps over a lazy dog.</p> </body>
The following figure shows examples of manipulating the text properties.
Figure: Text properties (in mobile applications only)
| Note |
|---|
| For a complete list of CSS Text Module Level 3 text properties (in mobile or wearable applications) and their possible values, see the Property index. |


