CSS Fonts Module Level 3: Manipulating Fonts
This tutorial demonstrates how you can modify fonts.
Warm-up
Become familiar with the CSS Fonts Module Level 3 API basics by learning about:
-
Manipulating Fonts
Control the appearance of text using the CSS font properties.
Manipulating Fonts
To enhance the user experience of your application, you must learn to handle fonts using CSS font properties:
-
Define the font-style property within a <style> element in the <head> section of the Web page to apply different font styles:
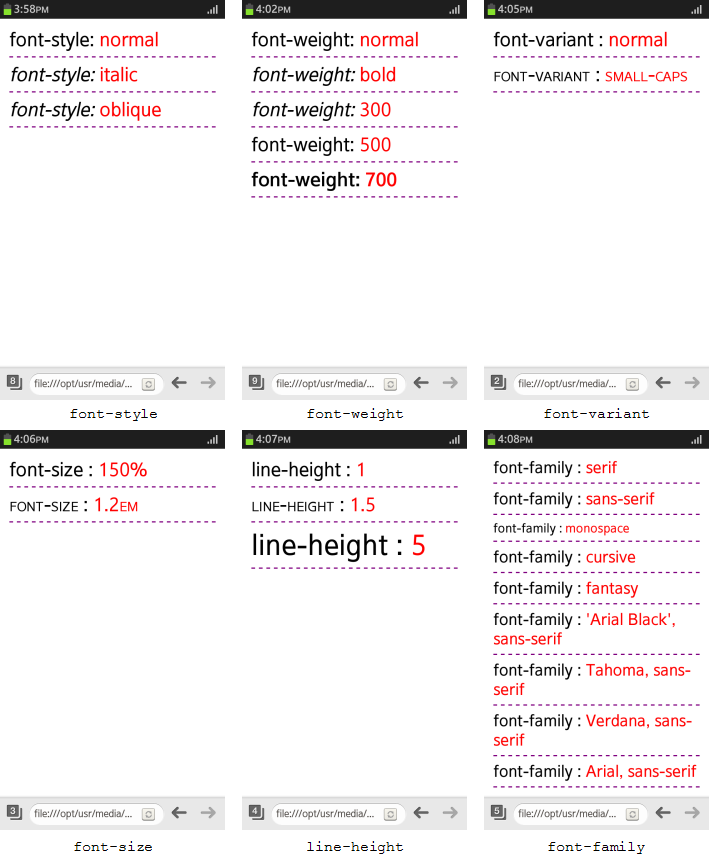
<head> <style> p:nth-child(1) em{font-style: normal} p:nth-child(2) em{font-style: italic} p:nth-child(3) em{font-style: oblique} </style> </head> <body> <p>font-style: <em>normal</em></p> <p>font-style: <em>italic</em></p> <p>font-style: <em>oblique</em></p> </body> -
Define the font-weight property, which controls the weight of the text:
<head> <style> p:nth-child(1) {font-weight: normal} p:nth-child(2) {font-weight: bold} p:nth-child(3) {font-weight: 300} p:nth-child(4) {font-weight: 500} p:nth-child(5) {font-weight: 700} </style> </head> <body> <p>font-weight: <em>normal</em></p> <p>font-weight: <em>bold</em></p> <p>font-weight: <em>300</em></p> <p>font-weight: <em>500</em></p> <p>font-weight: <em>700</em></p> </body> - Define the font-variant property to
change the font to, for example, use small capital letters:
<head> <style> p:nth-child(1) {font-variant: normal} p:nth-child(2) {font-variant: small-caps} </style> </head> <body> <p>font-variant: <em>normal</em></p> <p>font-variant: <em>small-caps</em></p> </body> - Define the font-size property, which controls the size of the font:
<head> <style> p:nth-child(1) {font-size: 150%} p:nth-child(2) {font-size: 1.2em} </style> </head> <body> <p>font-size: <em>150%</em></p> <p>font-size: <em>1.2em</em></p> </body> </html> - Define the line-height property, which controls the height of a text line:
<head> <style> p:nth-child(1) {line-height: 1} p:nth-child(2) {line-height: 1.5} p:nth-child(3) {line-height: 5} </style> </head> <body> <p>line-height: <em>1</em></p> <p>line-height: <em>1.5</em></p> <p>line-height: <em>5</em></p> </body> - Define the font-family property, which assigns a specific font or its representative to an element. The list order within the <style> element determines the property priority.
If the assigned font is not installed on the target, a different font is obtained based on the user system.
<head> <style> p:nth-child(1) {font-family: serif} p:nth-child(2) {font-family: sans-serif} p:nth-child(3) {font-family: monospace} p:nth-child(4) {font-family: cursive} p:nth-child(5) {font-family: fantasy} p:nth-child(6) {font-family: 'Arial Black', sans-serif} p:nth-child(7) {font-family: Tahoma, sans-serif} p:nth-child(8) {font-family: Verdana, sans-serif} p:nth-child(9) {font-family: Arial, sans-serif} </style> </head> <body> <p>font-family: <em>serif</em></p> <p>font-family: <em>sans-serif</em></p> <p>font-family: <em>monospace</em></p> <p>font-family: <em>cursive</em></p> <p>font-family: <em>fantasy</em></p> <p>font-family: <em>'Arial Black', sans-serif</em></p> <p>font-family: <em>Tahoma, sans-serif</em></p> <p>font-family: <em>Verdana, sans-serif</em></p> <p>font-family: <em>Arial, sans-serif</em></p> </body> </html>
The following figure shows examples of manipulating the text font properties.
Figure: Font properties (in mobile applications only)
| Note |
|---|
| For a complete list of CSS Fonts Module Level 3 font properties (in mobile or wearable applications) and their possible values, see the Property index. |


