Web: Managing Web Pages and Web Content
This tutorial demonstrates how you can create a simple Web browser.
Warm-up
Become familiar with the Web API basics by learning about:
-
Initializing the EFL WebKit
Initialize the EFL WebKit (EWK) for use.
-
Creating and Deleting a Window Object
Create and delete a window object.
-
Setting the Window Layout
Create the window layout.
-
Setting the Window View
Set the window smart view and settings.
-
Handling Key and Mouse Events
Handle the key and mouse event.
-
Showing a Window and Setting the Focus
Show a window and set the focus.
-
Finding a Window
Use the helper functions to find a window.
-
Finalizing the Application
Finalize the application.
Initializing the EWK WebKit
To initialize the EWK WebKit:
- To use the functions and data types of the WebView API (in mobile and wearable applications), include the <Ecore.h>, <Ecore_Evas.h>, <Ecore_Getopt.h>, <Eet.h>, <Eina.h>, <Elementary.h>, <Evas.h>, <EWebKit.h>, and <app.h> header files in your application:
#include <Ecore.h> #include <Ecore_Evas.h> #include <Ecore_Getopt.h> #include <Eet.h> #include <Eina.h> #include <Elementary.h> #include <Evas.h> #include <EWebKit.h> #include <app.h>
- To use the EWK API, an application needs the following privileges:
Table: Required privileges for an EWK application Privilege Description http://tizen.org/privilege/appmanager.launch Allows the application to open another application conditionally. http://tizen.org/privilege/content.write Allows the application to create, update and delete content. http://tizen.org/privilege/internet Allows the application to use the Internet connection. http://tizen.org/privilege/notification Allows the application to provide user notifications, such as messages and badges http://tizen.org/privilege/location Allows the application to use the user location data. http://tizen.org/privilege/camera Allows the application to manage the device cameras to preview and capture pictures. http://tizen.org/privilege/externalstorage Allows the application to access, read and write to the external storage. http://tizen.org/privilege/display Allows the application to access the display. http://tizen.org/privilege/network.get Allows the application to create a network connection. - The sample browser uses several Evas objects to build the browser UI. To easily manage the UI elements, use the Browser_window data structure. The browser window data is stored in a Browser_window structure that contains 2 Evas_Object instances.
typedef struct _Browser_Window { Evas_Object *elm_window; Evas_Object *ewk_view; Evas_Object *back_button; Evas_Object *forward_button; } Browser_Window; EXPORT_API int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int args = 1; Browser_Window window; memset(&window, 0x00, sizeof(Browser_Window)); ui_app_lifecycle_callback_s ops; memset(&ops, 0x00, sizeof(ui_app_lifecycle_callback_s)); ops.create = br_app_create; return ui_app_main(argc, argv, &ops, &window); } - To create a window, call the window_create() function in the br_app_create(void *browser) function.
window = window_create(NULL, 0, 0, EINA_FALSE);
Creating and Deleting a Window Object
To create and delete a window object:
- To create a window object, use the elm_win_add(Evas_Object* parent, const char* name, Elm_Win_Type type) function.
- You can add a Smart Callback to your window using the evas_object_smart_callback_add (Evas_Object * obj, const char * event, Evas_Smart_Cb func, const void * data) function.
- The function adds a callback to the event specified by the event on the smart object (smart event).
static Browser_Window *window_create(Evas_Object *opener, int width, int height, Eina_Bool view_mode) { // Allocate memory Browser_Window *window = calloc(1, sizeof(Browser_Window)); if (!window) { // "ERROR: could not create browser window." return NULL; } // If you want to use gpu acceleration, use the following function // elm_config_accel_preference_set("opengl:depth24:stencil8"); // Create window window->elm_window = elm_win_add(NULL, "minibrowser-window", ELM_WIN_BASIC); evas_object_smart_callback_add(window->elm_window, "delete,request", on_window_deletion, &window); } - An application also needs a callback fired for the Deletion Window Event. In the callback's body of implementation, call the window_close() function for a returned object of the window_find_with_elm_window() function.
static void on_window_deletion(void *user_data, Evas_Object *elm_window, void *event_info) { window_close(window_find_with_elm_window(elm_window)); }
Setting the Window Layout
Create the window layout.
Figure: Window layout
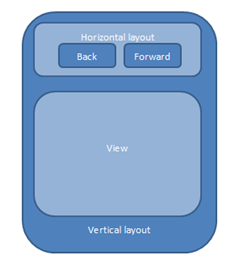
For this purpose, create new boxes (vertical_layout and horizontal_layout) using the elm_box_add() function:
// Create vertical layout Evas_Object *vertical_layout = elm_box_add(window->elm_window); elm_box_padding_set(vertical_layout, 0, 2); evas_object_size_hint_weight_set(vertical_layout, EVAS_HINT_EXPAND, EVAS_HINT_EXPAND); elm_win_resize_object_add(window->elm_window, vertical_layout); evas_object_show(vertical_layout); // Create horizontal layout for top bar Evas_Object *horizontal_layout = elm_box_add(window->elm_window); elm_box_horizontal_set(horizontal_layout, EINA_TRUE); evas_object_size_hint_weight_set(horizontal_layout, EVAS_HINT_EXPAND, 0.0); evas_object_size_hint_align_set(horizontal_layout, EVAS_HINT_FILL, 0.0); elm_box_pack_end(vertical_layout, horizontal_layout); evas_object_show(horizontal_layout);
The evas_object_size_hint_weight_set() function sets the hints for an object's weight. EVAS_HINT_EXPAND is a macro definition for a value 1.0 (EVAS_HINT_FILL for -1.0). The elm_win_resize_object_add(Evas_Object* obj, Evas_Object* subobj) function adds a subobj as the resize object of obj. The evas_object_show(Evas_Object* obj) function makes an obj visible. The elm_box_pack_end(Evas_Object* obj, Evas_Object* subobj) function adds a subobject at the end of the pack list.
Setting the Window View
Create a window view and set the user agent. To create the view, use the ewk_view_add() function. The view is an object that displays pages in the browser. To set the user agent, use the ewk_view_user_agent_set() function.
static Browser_Window *window_create(Evas_Object *opener, int width, int height, Eina_Bool view_mode)
{
Evas *evas = evas_object_evas_get(window->elm_window);
window->ewk_view = ewk_view_add(evas);
ewk_view_user_agent_set(window->ewk_view, user_agent_string);
}
Handling Key and Mouse Events
To handle mouse or key events, corresponding callbacks need to be set by calling the evas_object_event_callback_add() function.
static Browser_Window *window_create(Evas_Object *opener, int width, int height, Eina_Bool view_mode)
{
evas_object_event_callback_add(window->ewk_view, EVAS_CALLBACK_KEY_DOWN, on_key_down, window);
evas_object_event_callback_add(window->ewk_view, EVAS_CALLBACK_MOUSE_DOWN, on_mouse_down, window);
}
| Event | Callback | Callback type |
|---|---|---|
| Key down | EVAS_CALLBACK_KEY_DOWN | static void on_key_down(void *user_data, Evas *e, Evas_Object *ewk_view, void *event_info); |
| Mouse down | EVAS_CALLBACK_MOUSE_DOWN | static void on_mouse_down(void *user_data, Evas *e, Evas_Object *ewk_view, void *event_info); |
To handle pressed key modifiers, such as Control or Alt, the evas_key_modifier_is_set() function must be called. To get the Evas_Modifier object that contains information about which key modifiers are registered, call the evas_key_modifier_get() function, passing the Evas canvas object as an argument. Example code:
static void on_key_down(void *user_data, Evas *e, Evas_Object *ewk_view, void *event_info)
{
Browser_Window *window = (Browser_Window *)user_data;
Evas_Event_Key_Down *ev = (Evas_Event_Key_Down*) event_info;
const Evas_Modifier *mod = evas_key_modifier_get(e);
Eina_Bool ctrlPressed = evas_key_modifier_is_set(mod, "Control");
Eina_Bool altPressed = evas_key_modifier_is_set(mod, "Alt");
}
Now ev->key contains the name of the key that caused the event trigger. For example, to check whether the combination Alt + Left Arrow was pressed, (!strcmp(ev->key, "Left") && altPressed) must evaluate to TRUE.
| Key | Behavior | API |
|---|---|---|
| Alt+Left | Back view | ewk_view_back |
| Alt+Right | Forward view | ewk_view_forward |
| F5 | Reload view | ewk_view_reload |
| Alt+F5 | Reload view bypassing cache | ewk_view_bypass_cache |
| F6 | Stop | ewk_view_stop |
The mouse down event information is stored in Evas_Event_Mouse_Down. Similarly as in key events, ev->button contains information on which button was pressed. In this example, pressing the first button calls the view_focus_set() function to update the focus. Example code:
static void on_mouse_down(void *user_data, Evas *e, Evas_Object *ewk_view, void *event_info)
{
Browser_Window *window = (Browser_Window *)user_data;
Evas_Event_Mouse_Down *ev = (Evas_Event_Mouse_Down *)event_info;
if (ev->button == 1)
view_focus_set(window, EINA_TRUE);
}
Showing a Window and Setting the Focus
In EFL, the UI focus control is implemented in an Elementary object, not an Evas_object. Therefore, the application using EWK derived from an Evas_object must control the focus itself. For example, steal focus away from the elm_window object and give it to the ewk_view.
To set the focus to a ewk_view, use the void elm_object_focus_set (Evas_Object *obj, Eina_Bool focus) and void evas_object_focus_set (Evas_Object *obj, Eina_Bool focus) functions. Example code:
static void view_focus_set(Browser_Window *window, Eina_Bool focus)
{
// We steal focus away from elm focus model and start to do things
// manually here, so elm now has no clue what is up. Tell elm that its
// top level UI component is to be unfocused so elm gives up the focus
elm_object_focus_set(elm_object_top_widget_get(window->elm_window), EINA_FALSE);
evas_object_focus_set(window->ewk_view, focus);
};
Call this function in the window_create() function.
window_create()
{
elm_win_resize_object_add(window->elm_window, window->ewk_view);
evas_object_show(window->ewk_view);
evas_object_show(window->elm_window);
view_focus_set(window, EINA_TRUE);
return window;
}
The void evas_object_show (Evas_Object *obj) function makes the given Evas object visible.
Finding a Window
This example uses 2 helper functions for finding window structures. The first one, the window_find_with_elm_window() function, takes elm_window as an argument and returns a pointer to the Browser_Window object that the window is part of. The second one, the window_find_with_ewk_view() function, does the same for ewk_view. Both of them use the EINA_LIST_FOREACH macro to iterate over the windows list.
static Browser_Window *window_find_with_elm_window(Evas_Object *elm_window)
{
Eina_List *l;
void *data;
if (!elm_window)
return NULL;
EINA_LIST_FOREACH(windows, l, data)
{
Browser_Window *window = (Browser_Window *)data;
if (window->elm_window == elm_window)
return window;
}
return NULL;
}
static Browser_Window *window_find_with_ewk_view(Evas_Object *ewk_view)
{
Eina_List *l;
void *data;
if (!ewk_view)
return NULL;
EINA_LIST_FOREACH(windows, l, data)
{
Browser_Window *window = (Browser_Window *)data;
if (window->ewk_view == ewk_view)
return window;
}
return NULL;
}
Finalizing the Application
To close the application correctly, use the ewk_shutdown() function. This function cleans up any resources your application has allocated.
static void br_app_terminate(void *app_data)
{
ewk_shutdown();
}
In the main function, register the termination callback:
main()
{
ops.create = br_app_create;
ops.terminate = br_app_terminate;
return ui_app_main(argc, argv, &ops, &window);
}


