dlog
The dlog logging service consists of the dlogutil dlog library, and it supports sending log messages to a circular log device. The log device is a circular buffer used to collect log messages from various applications and the system.
The dlog service sends a log message to the circular buffer with APIs, including Priority and Tag information. With this information, it is easy to filter and check the messages with dlogutil.
Before using dlog, you should know which priorities and tags to use and where to write (format, buffer).
Priority
The priority level indicates the urgency of the log message.
| Priority | Description |
|---|---|
| DLOG_DEBUG | Log message which the developer wants to check |
| DLOG_INFO | Normal operational message |
| DLOG_WARN | Not an error, but a warning that an error will occur if action is not taken |
| DLOG_ERROR | An error |
For each log level (info, debug, and error), there is a separate macro:
- Info
Use dlog_print(or dlog_vprint) function with DLOG_INFO priority when you need info messages to be displayed with a specified tag.
// Print the "Initialization successful." info message with the tag to the console dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, "MyTag", "Initialization successful.");
- Debug
Use dlog_print(or dlog_vprint) function with DLOG_DEBUG priority when you need debug messages to be displayed with a specified tag.
// Print the debug message "string: Test" to the console dlog_print(DLOG_DEBUG, "MyTag", "string:","%s", "Test");
- Error
Use dlog_print(or dlog_vprint) function with DLOG_ERROR priority when you need error messages to be displayed with a specified tag.
if (something_wrong) { // Print the error message with the tag to the console dlog_print(DLOG_ERROR, "MyTag", "An unexpected error occurred"); } - Warning
Use dlog_print(or dlog_vprint) function with DLOG_WARN priority when you need warning messages to be displayed with a specified tag.
// Print the warning message with the tag to the console dlog_print(DLOG_WARN, "MyTag", "warning!");
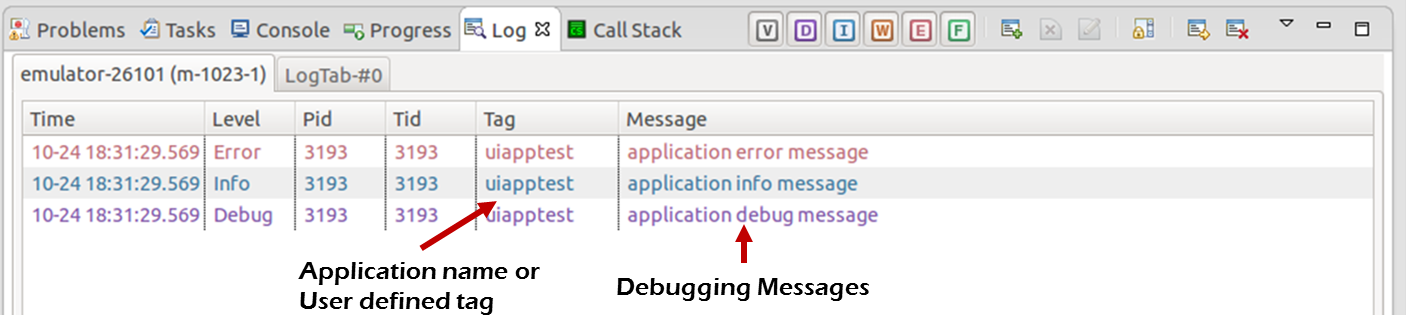
Log macros belong to Info, Debug, Error, and Warn log levels. To filter logs based on their levels, select the applicable log type in the Log view. You can also search logs by keywords, such as Pid, Tid, Tag, and Message. The following figure shows the output of a log macro.
Figure: Log macro output
Tag
A tag is used to identify the source of the log message.
There are no naming limitations, but do not forget that the tag is an identification of a module.
Each tag must be unique.
Error Type
| Numerator | Description |
|---|---|
| DLOG_ERROR_NONE | Successful |
| DLOG_ERROR_INVALID_PARAMETER | Invalid parameter |
| DLOG_ERROR_NOT_PERMITTED | Operation not permitted |
To send a log message:
#include <dlog.h>
int main(void)
{
int integer = 21;
char string[] = "test dlog";
dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, "USR_TAG", "test dlog");
dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, "USR_TAG", "%s, %d", string, integer);
return 0;
}
#include <dlog.h>
void my_debug_print(char *format, ...)
{
va_list ap;
va_start(ap, format);
dlog_vprint(DLOG_INFO, "USR_TAG", format, ap);
va_end(ap);
}
int main(void)
{
my_debug_print("%s", "test dlog");
my_debug_print("%s, %d", "test dlog", 21);
return 0;
}
Error Handling with dlog
Typical error handling example is as follows:
location_manager_h location_handle;
int result = location_manager_create(LOCATION_METHOD_GPS, location_handle);
if (result != LOCATIONS_ERROR_NONE)
{
dlog_print(DLOG_INFO, "MyTag", "Creation of the location manager failed.");
return false;
}
While working with the SDK this information is available in the Log tab. While working with the target device, one can also use dlogutil utility.
dlogutil
You can collect and print out logs with logutil. Logutil supports filtering, and managing the log device.
Using Logutil Commands
You can use a logutil command to view and follow the content of the log buffers. The general usage is:
dlogutil [<option>] ... [<filter-spec>] ...
Filtering Log Output
Every log message has a tag and a priority associated with it.
The filter expression follows the tag:priority format, where the tag indicates the tag of interest and the priority indicates the minimum level of priority to report for that tag. You can add any number of tag:priority specifications in a single filter expression.
The tag of a log message is a short name indicating the system component from which the message originates.
The priority is one of the following character values, ordered from the lowest to the highest priority:
- D - debug
- I - info
- W - warning
- E - Error
For example, if you want to see all log messages with the MyApp tag that are above the debug priority:
# dlogutil MyApp:D
If you want to see all log messages above the info priority:
# dlogutil *:I
Controlling Log Output Format
The log messages contain a number of metadata fields in addition to tag and priority. You can modify the output format for messages so that they display a specific metadata field. To do so, use the -v option when starting dlogutil and specify one of the supported output formats:
- brief: Displays the priority/tag and PID of the originating process (the default format)
- process: Displays the PID only
- tag: Displays the priority/tag only
- thread: Displays the process:thread and priority/tag only
- raw: Displays the raw log message, with no other metadata fields
- time: Displays the date, invocation time, priority/tag, and PID of the originating process
- long: Displays all metadata fields and separates messages with blank lines
# dlogutil [-v <format>]
List of Logutil Command Options
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| -b <buffer> | Alternates the log buffer. The main buffer is used by the default buffer. |
| -c | Clears the entire log and exits |
| -d | Dumps the log and exits |
| -f <filename> | Writes the log to <filename>. The default filename is stdout. |
| -g | Prints the size of the specified log buffer and exits |
| -n <count> | Sets the maximum number of rotated logs to <count>. The default value is 4. Requires the -r option. |
| -r <Kbytes> | Rotates the log file every <Kbytes> of output. The default value is 16. Requires the -f option. |
| -s | Sets the default filter spec to silent |
| -v <format> | Sets the output format for log messages. The default format is brief. |
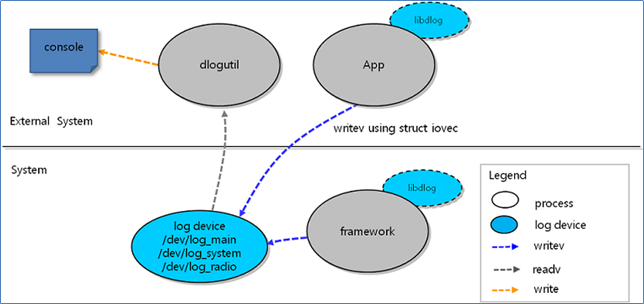
Architecture
The following figure illustrates the general architecture of the dlog logging service.
Figure: Architecture